Fermentation / Anaerobic Respiration
Key Questions
-
Answer:
Some examples of anaerobic respiration include alcohol fermentation, lactic acid fermentation.
Explanation:
Some examples of anaerobic respiration include alcohol fermentation, lactic acid fermentation (which can result in yogurt and in sore muscles), and in decomposition of organic matter. The equation is: glucose + enzymes = carbon dioxide + ethanol/lactic acid.
-
Answer:
Fermentation is an anaerobic metabolic process in which an organism converts a carbohydrate to an alcohol or an acid.
Explanation:
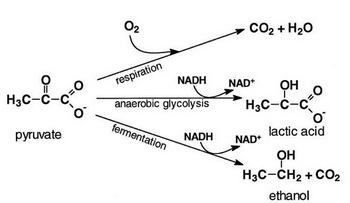
The first step in all fermentation processes is glycolysis, the conversion of glucose to pyruvate:
#"C"_6"H"_12"O"_6 → "2CH"_3"COCOO"^(−) + "2H"_2"O" + 2"H"^+# There are two main types of fermentation; one converts pyruvate into lactate (lactic acid) and the other into ethanol.
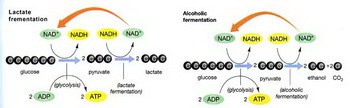
(from sun.menloschool.org)In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid.
#underbrace("CH"_3"COCOO"^-)_color(red)("pyruvate") stackrelcolor (blue)("enzymes")(→) underbrace("2CH"_3"CH(OH)COOH")_color(red)("lactic acid") # In alcohol fermentation,the pyruvate is decarboxylated to acetaldehyde, and then into ethanol.
#"CH"_3"COCOO"^(-)+ "H"^+ stackrelcolor (blue)("pyruvate decarboxylase")(→) "CH"_3"CHO" + "CO"_2# #"CH"_3"CHO" stackrelcolor (blue)("alcohol dehydrogenase")(⇌) "CH"_3"CH"_2"OH"# In an aerobic process, the pyruvate is converted by respiration to carbon dioxide and water.
Here is a summary of the three possible fates of pyruvate: