Step 1. Write the chemical equation
#"KOH + HI" → "KCl" + "H"_2"O"#
Step 2. Calculate the volume to reach the equivalence point
#color(blue)(bar(ul(|color(white)(a/a)c_text(A)V_text(A)= c_text(B)V_text(B)color(white)(a/a)|)))" "#
#V_text(B) = V_text(A) × c_text(C)/c_text(B) = "10.00 mL" × (0.125 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mol/L"))))/(0.100 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mol/L")))) = "12.5 mL"#
The equivalence point is at 12.5 mL #"KOH"#.
Step 3. pH during titration
(i) At 0.000 mL
#["H"_3"O"^"+"] = "0.125 mol/L"#
#"pH" = "-log"(0.125) = 0.90#
(ii) pH at 3.125 mL
#"Initial moles of HI" = 10.0 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mL HI"))) × ("0.125 mol I")/(1 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mL HI")))) = "1.25 mmol HI"#
#"Moles of KOH added " = 3.125 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mL KOHl"))) × "0.100 mmol KOH"/(1 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mL KOH")))) = "0.3125 mmol KOH"#
#"Moles of HI remaining" = "(1.25 - 0.3125) mmol HI = 0.938 mmol HIH"#
#"Volume = (10.00 + 3.125) mL = 13.12 mL"#
#["H"_3"O"^"+"] = "0.938 mmol"/"13.12 mL" = "0.0714 mol/L"#
#"pH = -log(0.0714) = 1.15"#
(iii) pH at 6.25 mL
#"Moles of KOH added " = 6.25 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mL KOHl"))) × "0.100 mmol KOH"/(1 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mL KOH")))) = "0.625 mmol KOH"#
#"Moles of HI remaining" = "(1.25 - 0.625) mmol HI = 0.625 mmol HIH"#
#"Volume = (10.00 + 6.25) mL = 16.25 mL"#
#["H"_3"O"^"+"] = "0.625 mmol"/"16.25 mL" = "0.0385 mol/L"#
#"pH = -log(0.0385) = 1.41"#
(iv) pH at 11.50 mL
#"Moles of KOH added " = 11.50 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mL KOHl"))) × "0.100 mmol KOH"/(1 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mL KOH")))) = "1.15 mmol KOH"#
#"Moles of HI remaining" = "(1.25 - 1.15) mmol HI = 0.10 mmol HIH"#
#"Volume = (10.00 +11.50) mL = 21.50 mL"#
#["H"_3"O"^"+"] = "0.10 mmol"/"21.5 mL" = "0.004 65 mmol/L"#
#"pH = -log(0.004 65) = 2.33"#
(v) pH at 12.50 mL
You are at the equivalence point.
#"pH = 7.00**
(vi) pH at 13.50 mL
You are 1.00 mL past the equivalence point, so you have neutralized all the #"HI"# and have a solution of excess #"KOH"#.
#" Excess moles KOH " =1.00 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mL KOH"))) × "0.100 mmol KOH"/(1 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mL KOH")))) = "0.100 mmol KOH"#
#"Volume = (10.0 + 13.50) mL = 23.50 mL"#
#["OH"^"-"] = "0.100 mmol"/"23.50 mL" = "0.004 25 mmol/L"#
#"pOH = -log(0.004 25) = 2.37"#
#"pH = 14.00 -pOH = 14.00 - 2.37 = 11.62"#
(vii) pH at 18.75 mL
You are 6.25 mL past the equivalence point, so you have neutralized all the #"HI"# and have a solution of excess #"KOH"#.
#" Excess moles KOH " =6.25 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mL KOH"))) × "0.100 mmol KOH"/(1 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mL KOH")))) = "0.625 mmol KOH"#
#"Volume = (10.0 + 18.75) mL = 28.75 mL"#
#["OH"^"-"] = "0.625 mmol"/"28.75 mL" = "0.0217 mmol/L"#
#"pOH = -log(0.0217) = 1.66"#
#"pH = 14.00 -pOH = 14.00 - 1.66 = 12.33"#
Step 4. Construct the titration curve
Plot the points on a graph and draw a smooth curve between them.
Your graph should look something like this.
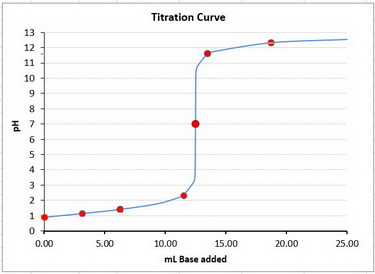
I marked your points with the red dots.



