Why is a monosodium phosphate solution acidic?
2 Answers
Mono sodium fosfate is one of three sodium salts that can be formed from fosforic acid:
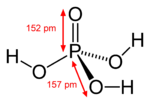
As you will see, the three hydrogen ions (
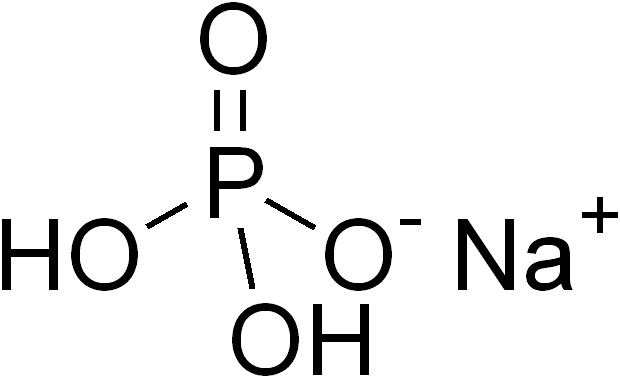
The
(pictures from Wikipedia)
An aqueous solution of NaH₂PO₄ is acidic because the H₂PO₄⁻ ion is a stronger acid than a base. The Na⁺ ion acts only as a spectator ion to balance the charge.
When you dissolve NaH₂PO₄ in water, it dissociates into ions.
NaH₂PO₄(s) → Na⁺(aq) + H₂PO₄⁻(aq)
The H₂PO₄⁻ ion is amphoteric. It can act as either an acid or a base.
The equation for its reaction as an acid is
H₂PO₄⁻ + H₂O ⇌ HPO₄²⁻ + H₃O⁺;
The equation for its reaction as a base is
H₂PO₄⁻ + H₂O ⇌ H₃PO₄ + OH⁻;
Since
This means that solutions of NaH₂PO₄ will be acidic.


