Question #3bdfe
1 Answer
Humidity increases.
Explanation:
Atmospheric pressure is the weight of the mass of atmosphere over a certain point. As a parcel of air rises in the atmosphere there is less air above it. Since there is less mass there is less weight and therefore pressure drops.
According to Gay Lussac's law, pressure and temperature are proportionate. Therefore if the pressure drops the air parcel must cool.
The amount of water vapor that can be held in an air parcel is a function of the temperature. Warmer air holds more water vapor. The maximum amount of water that an air parcel can hold at a given temperature is the saturation point or the point that the relative humidity reaches 100%.
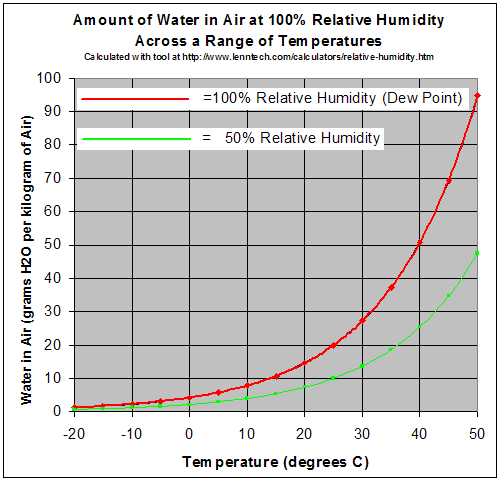
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relative_humidity
This chart shows what the humidity is for a certain amount of water at a given temperature. So if you have 10g of water vapor per kilogram of air at 25 degrees C, you are at 50% relative humidity.
If an air parcel rises it will cool at a rate of 10 degrees per 1000 meters of elevation. That is known as the dry adiabatic lapse rate. Adiabatic simply means that the air in the parcel does not mix with the surrounding air. Therefore if the parcel of air at 25 degrees and 10g of water per kilogram of air rises 100 meters it will cool to a temperature of 15 degrees. At 15 degrees that amount of water vapor is actually the maximum amount the air can hold or 100% relative humidity.
At 100 percent relative humidity, if the air cools any further the amount of water that the air can hold will decrease. If the example parcel rose another 1000m it would be a temperature of 5 degrees. At 5 degrees the maximum amount of water vapor the air can hold per kilogram is about 8g. So what happens to the other 2 grams?
Those 2 grams of water vapor that the air cannot hold, are therefore changed into liquid water. This liquid water will be in the form of cloud.
