Help w/ Quadratic Equations 2?
Help w/ Quadratic Equations 2?
Hi Can you please solve the following solve for r , please be visual and show your work!
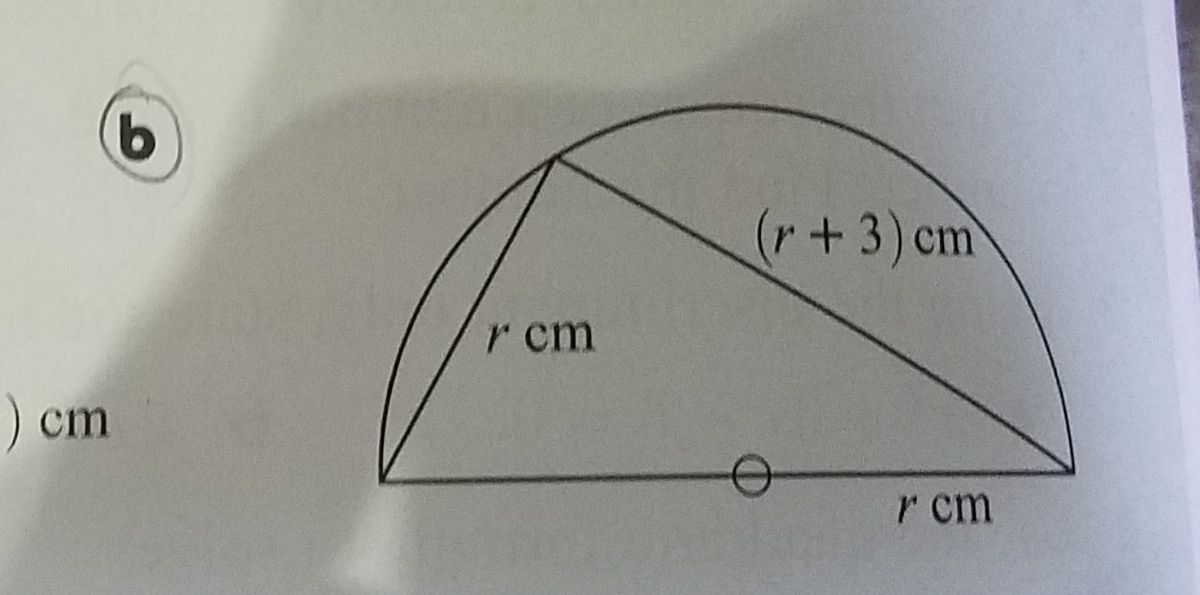
Help w/ Quadratic Equations 2?
Hi Can you please solve the following solve for r , please be visual and show your work!
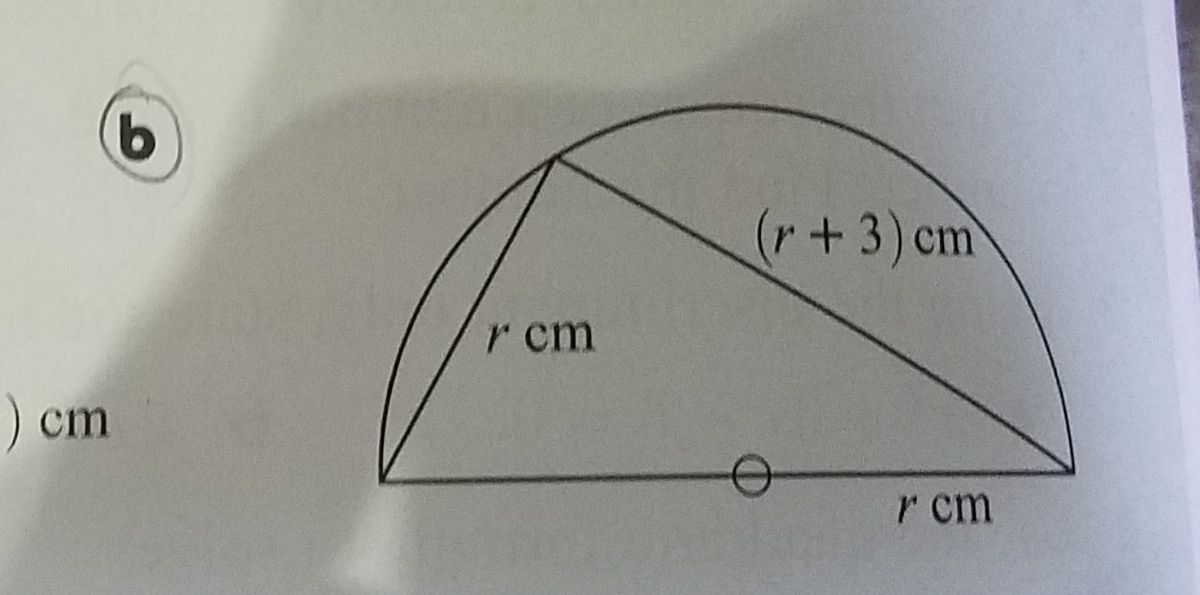
2 Answers
Explanation:
Since this triangle has the diameter of the circle as its longest side, it must be a right triangle. Since the radius is
#(r)^2+(r+3)^2=(2r)^2#
Now we need to expand each of these terms.
#r^2 + (r^2+6r+9) = 4r^2#
And simplify.
#2r^2 + 6r + 9 = 4r^2#
Now, subtract
#0 = 2r^2 - 6r - 9#
There are no factors of
#r = (-(-6) +- sqrt((-6)^2-4(2)(-9)))/(2(2))#
#r = (6 +- sqrt(36+72))/4 = (6 +- sqrt108)/4#
#r = (6+-6sqrt3)/4 = (3+-3sqrt3)/2#
#r = (3+3sqrt3)/2 " "# or#" " r = (3-3sqrt3)/2#
So we have two solutions. However, the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle cannot be negative. This rules out the second solution.
Therefore,
Final Answer
The value of
Explanation:
The triangle is a right angle triangle.
So, we can apply Pythagoras ' theorem
The discriminant is
As
The 2 solutions are
We keep only


