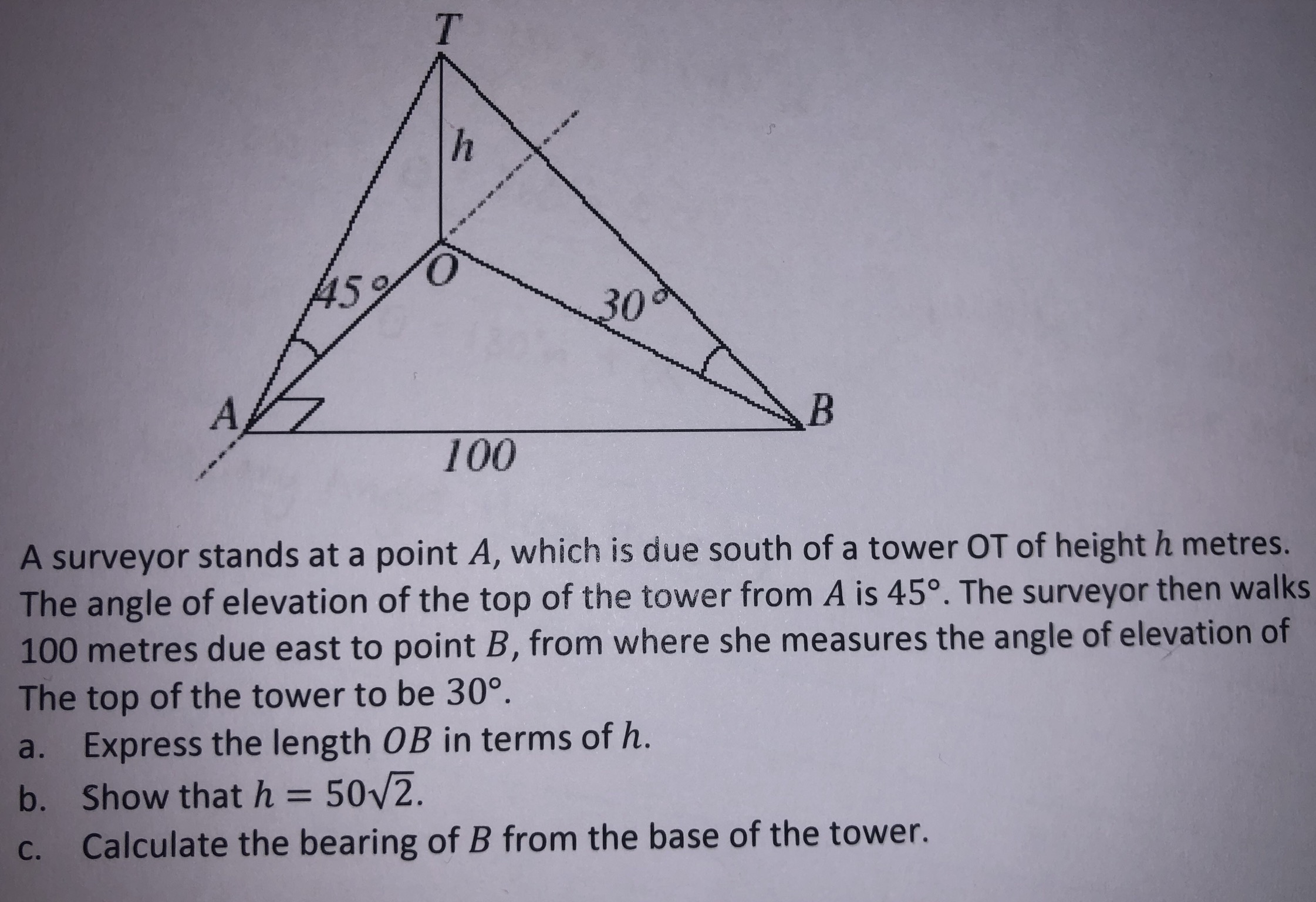
How to do the following? I NEED HELP !
2 Answers
Below
Explanation:
a. The
b. Similarly,
Since you have already find the side OB and OA, then you can make use the right angled
Using pythagoras theorem,
Now, since h is a height then
so
c. "bearing of B from the base of the tower" is in other words "find the
From a, we found that
So subbing in
We can find
So
Therefore, the bearing of B from the base of the tower is 90
Again
In
So by Pythagoras theorem
Again
So bearing of B from base of the tower


