How to do this question?
2 Answers
Explanation:
Part (a) :
At the stationary points,
Hence,
Part (b) :
Since at the stationary point,
tangent at that point is zero. So, it is a horizontal line
through the stationary point
Thus, the eqn. the tgt. is
Part (c) :
Suppose that, at the point
curve is
But, the gradient of the curve at
Observe that, the sum of the co-effs. is
Since reqd.
The corresponding
Hence,
a)
b)
c)
Explanation:
A stationary point is a point where the derivative of the function vanishes. Given then the equation of the curve:
evaluate its first derivative using the quotient rule:
and solve the equation:
The corresponding value of
The coordinates of the stationary point
By definition in a stationary point the tangent is horizontal because the derivative is null, so the equation of the tangent to the curve in
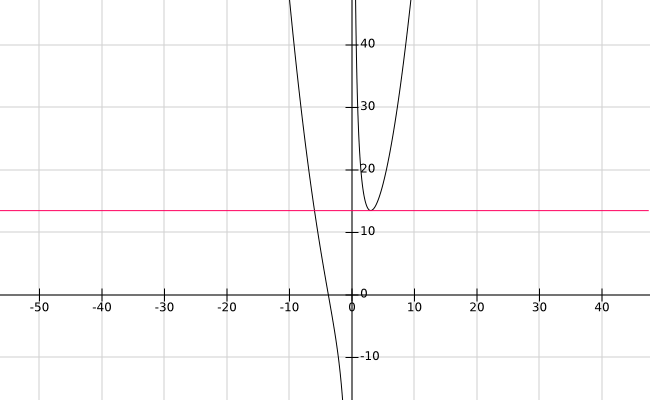
Finally, the value of the gradient of a scalar function is the value of its derivative so we can find the point where the value of the gradient is
We can easily see that
and as the roots of:
must be negative, we can conclude that the solution is

