1) How do enzymes actually work to speed up chemical reactions?
1 Answer
Apr 30, 2018
Enzymes act as catalysts and therefore provide an alternate route for the reaction with a lower activation energy.
Explanation:
In collision theory, in order for a successful reaction to take place, the molecules must collide with correct geometry and with energy higher than the activation energy.
Enzymes are biological catalysts provide alternate routes for a reaction which make successful reactions more likely to occur.
Hence, the enthalpy diagram with a catalyst looks different from without the catalyst:
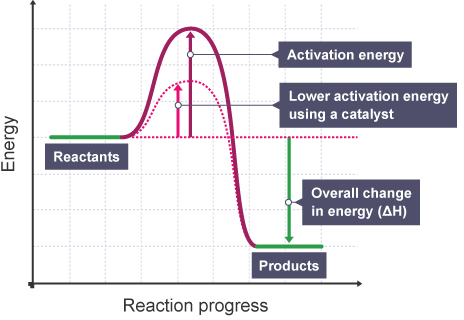
Which implies that because the energy threshold for a successful reaction to occur is lower, the probability that more molecules will react per unit time increases, which translates to an increased rate of reaction.