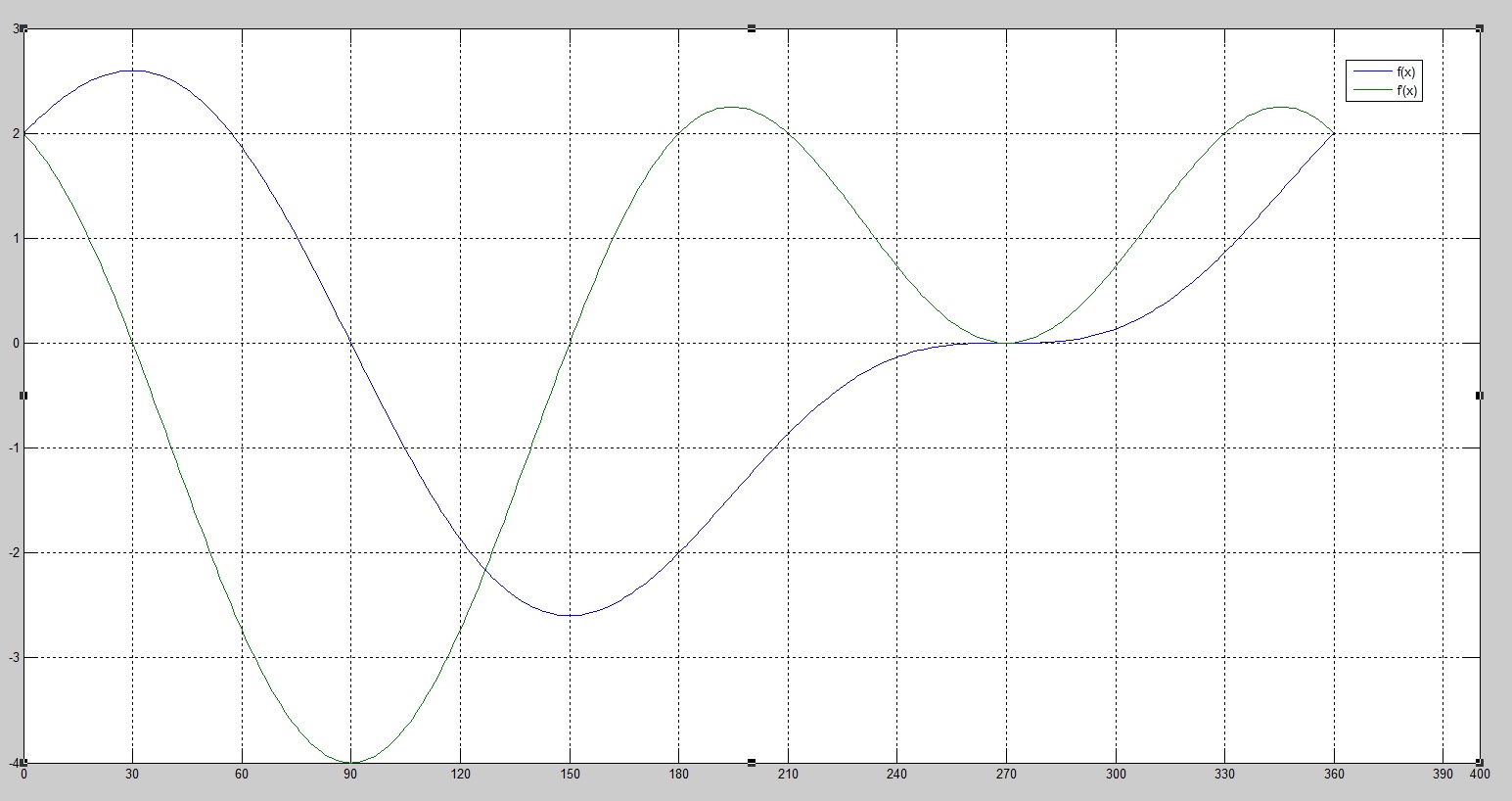
Derivation is given below
# f(x) = 2cosx+sin2x#
#f'(x) = -2sinx+2cos2x#
#f''(x) = -2cosx-4sin2x#
First derivative test is to find values of #x# when #f'(x) = 0#.
So we have
#-2sinx+2cos2x = 0#
diving by 2 and substituting #cos2x = 1-2sin^2x# gives
#1-2sin^2x-sinx = 0#
or
# 2sin^2x+sinx-1 = 0#
Let #t = sinx# then
#2t^2+t-1 =0#
#t=(-1+-sqrt(1^2-4*2*(-1)))/(2*2)#
#t = (-1+-3)/4#
#t=-1 or t=1/2#
Case 1
#t=1/2# then #sin x = 1/2#
This gives two values in the interval #[0,2pi]#
#x=pi/6 or x=(5pi)/6#
The sign of second derivative tells us about the nature of inflection point. To test the theory let us take the first value of x.
# x = pi/6 #
then
#f''(x) |_ (x=pi/6) = -2*cos(pi/6)-4*sin((2pi)/6)#
# = -2*sqrt(3)/2-4*sqrt(3)/2#
#=-3*sqrt(3)#
As #f''(x)# value is negative the function is maximum at #pi/6#
The value is
#f(x) = 2*cos(pi/6)+sin((2*pi)/6)#
# = 2*sqrt(3)/2+sqrt(3)/2#
# = (3*sqrt(3))/2#
#=2.5981#
at #f''(x) |_ (x=(5pi)/6) = 5.1962#
Hence #f(x)# is minimum at #x=(5pi)/6# and the value is #-2.5981#
Case 2
# t=-1# then # sin x = -1#
and this gives an x value of #(3pi)/2#
#f''(x) |_ (x=(3pi)/2) = -2*cos((3pi)/2)-4*sin((6pi)/2)#
#f''(x) |_ (x=(3pi)/2)=-2*0-4*0#
#f''(x) = 0#
Hence the point is neither minimum nor maximum.
Find attached the calculated graph for #f(x) and f'(x)#.