Question #8ea79
1 Answer
You have three variables,
You get a 3D surface that looks like the middle graph in the image below.
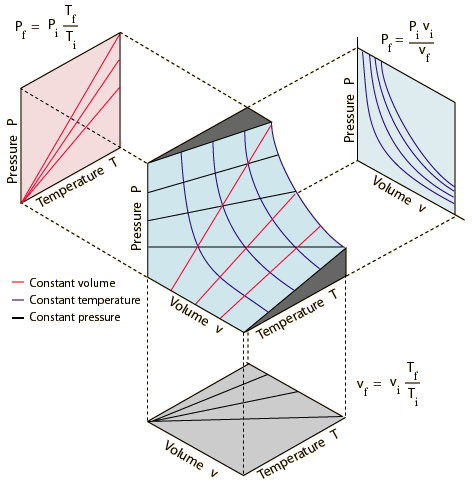
If the temperature is constant and you look at the graph in a
If the pressure is constant and you look at the graph in a
If the volume is constant and you look at the graph in a
Put them all together, and the 3D surface is a graph of the Combined Gas Law,


