Question #183b2
1 Answer
What is a diverging Mirror ?
Convex mirror is a diverging mirror. The parallel beam of light turns into divergent beam after reflection on a convex mirror as shown in the ray diagram below.
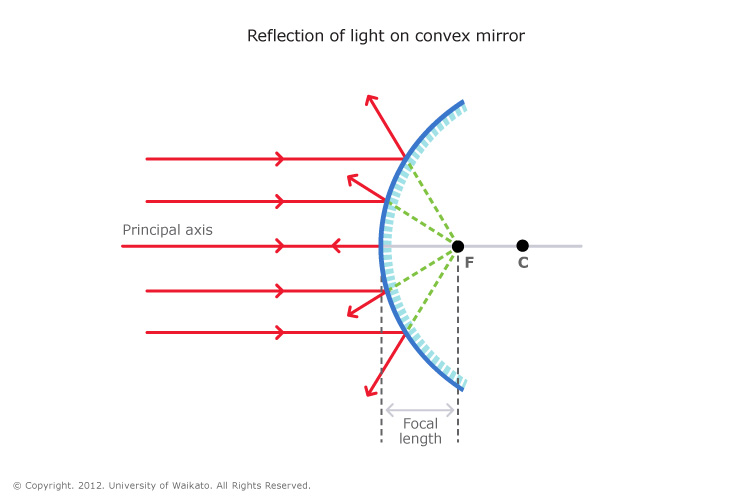
Actually it occurs due to increase in the angle of incidence of the ray as it is shifted away from principal axis. On observation of the ray diagram what we see that the incident ray at the middle is along the normal i.e. inclined at
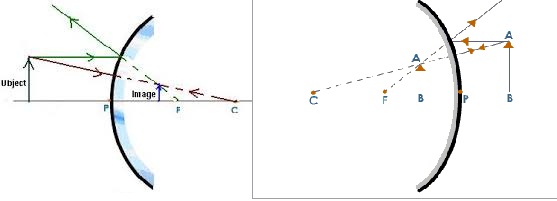
Due to this property of convex mirror it always produces diminished virtual image whereas convex mirror produces magnified virtual image. So a convex mirror can easily be identified by this property of formation diminished virtual image
Refraction
When a ray of light enters in one transparent medium from other its velocity changes. This change in velocity always occurs if the medium in which the ray enters, differs from the medium from which it comes. It does not depend on the angle of incidence.
The deviation of ray during refraction is observed only in case of oblique incidence of the ray but change in velocity always occurs.
By wave theory of light the refractive index is related with the velocity of light in the pair of media concerned as follows.
The refractive index of medium 2 w.r to medium 1
This relation holds good for normal incidence also. But Snell's is not valid for normal incidence of ray.
So we can say the refraction always occurs when a ray of light enters from one medium to another medium even if the incidence is normal to the interface.

