Question #026bf
2 Answers
Explanation:
To find out the resultant Resistance please refer the Image below which gives better illustration about the diagram 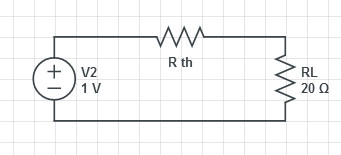
now instead of directly substituting the values we we use there names .
and
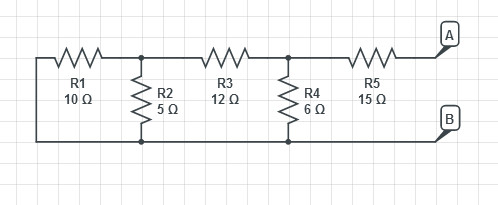
The resistance across A and B gives the value of Thevenin’s resistance or
Explanation:
To find the Thevenin Voltage, you remove the load and then compute the open circuit voltage across the two points
Summing the voltages around the first window:
Summing the voltages around the second window:
Substituting values:
Multiply equation [4] by 3 and add to equation [3]:
Because no current flows through
To find the Thevenin equivalent resistance, we replace the voltage source with a wire and compute the equivalent resistance:
