Question #68518
1 Answer
Explanation:
From the reaction above we get to know that Bromine is the leaving group.And as a rule which is applicable to most elimination reactions the H must be in an anti position to the leaving group means either the hydrogen will be pointing up and the bromine atom pointing down and vice versa. It depends from the way from you look at the molecule.
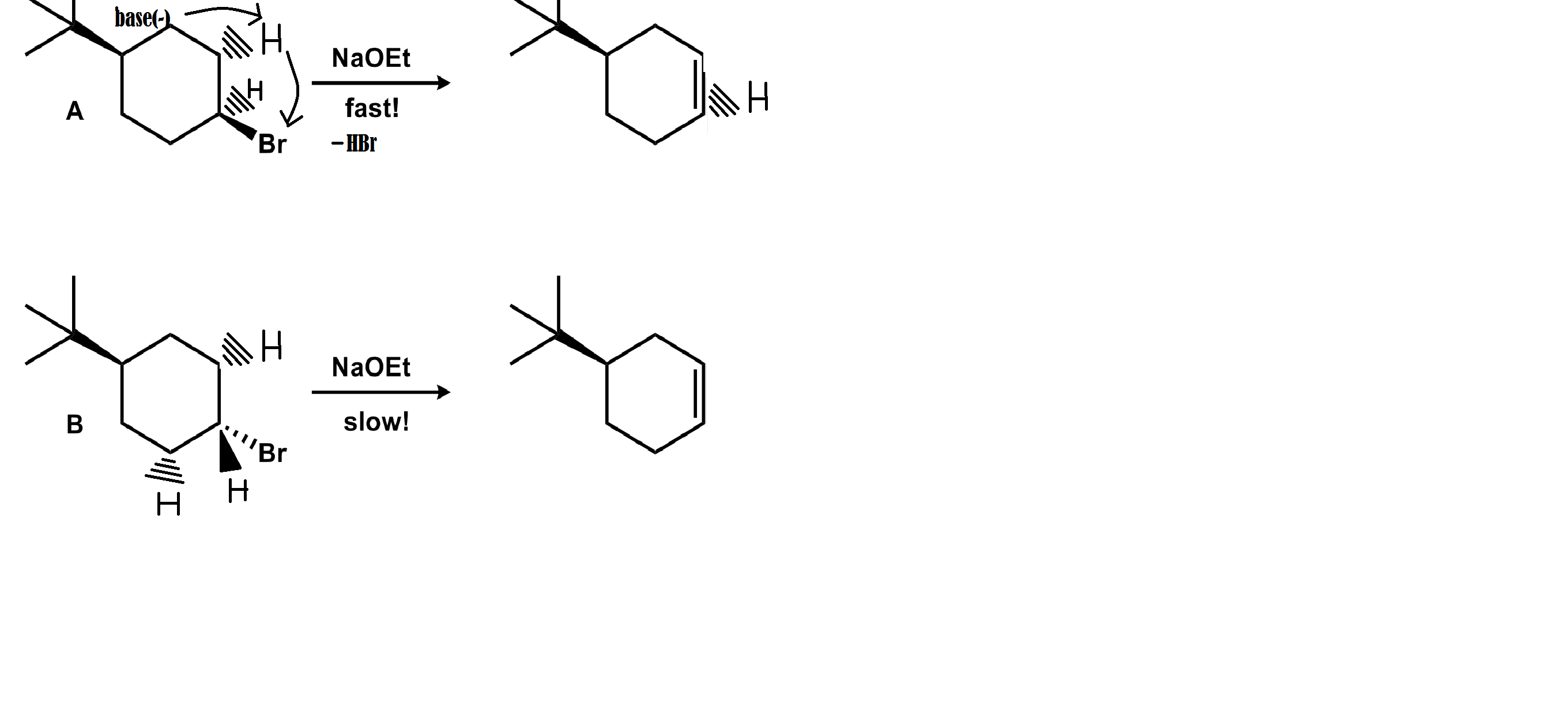
In this E2 reaction a base comes in between a hydrocarbon bond and absconds a proton from the hydrogen atom leaving a lone pair on the carbon atom. This lone pair goes to a electrophilic antibond which is quit polar and kicks out the negative ion which reacts with the absconded proton to form an acid.
In this case electrophilic antibond is C-Br and the negative ion is a Bromine atom and the acid is
In the trans case everything is same except the the location of Br atom and the hydrogen atom . The E2 reaction in the cis isomer is faster because in the cis isomer the hydrogen and Br face each other diagonally and this reaction is more favourable and therefore faster. Otherwise, Br and H is at syn position in the trans isomer, which makes it nearly impossible to react.

