Question #a8a17
1 Answer
the answer is B.
I know this explanation is very long, but bear with me. This is an important basic concept for any biology course, so a good foundation is important.
Explanation:
To make proteins, first DNA is translated into a complementary strand of messenger RNA (commonly known as mRNA), which is created using the same complements as DNA (A-T / C-G). However, instead of thymine (T) RNA uses uracil (U).
So in this example, the mRNA strand would be:
U-U-C-C-C-G-G-A-A-U-A-G
Next, this strand of mRNA goes to the ribosome where its code is used to make proteins. The bases are read in groups of threes, called codons.
Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules have anticodons (a sequence complementary to the codons). They also carry the appropriate amino acid which corresponds with their anticodon. tRNA molecules look for a sequence which complements theirs on the mRNA. Then they "drop off" the amino acid, which bonds with other amino acids to make a protein.
The yellow is tRNA, the pink is amino acids, and the mint green is mRNA.
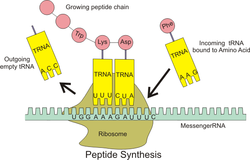
Each codon codes for a specific amino acid. Your teacher may have given the class a reference chart to use, but you can easily find one online. Here is one: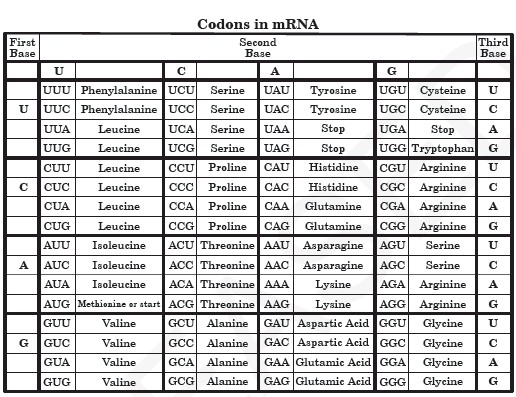
(The chart gives the sequence of mRNA, not tRNA.)
Remember the mRNA strand from before is
U-U-C-C-C-G-G-A-A-U-A-G.
So the codons are (UUC) (CCG) (GAA) (UAG).
In the chart, you can see that
(UUC) codes for Phenylalanine,
(CCG) codes for Proline,
(GAA) codes for Glutamic acid, and
(UAG) codes for stop.
(stop obviously isn't an amino acid, it tells the system to finish the translation process.)
In this example, a tRNA molecule will come with an anticodon of (AAG) and carrying Phenylalanine. It will find the (UUC) sequence on the mRNA and once it does, it will "drop off" the Phenylalanine. Then the next tRNA molecule will come and do the same thing and drop off Proline. Proline will bond with the Phenylalanine and so on.
So the protein is :
Phenylalanine - Proline - Glutamic acid
Glutamic acid is the same as glutatmate. So the answer is B.

