Question #24f89
1 Answer
If they are added along the same axis..
Explanation:
I'll assume you mean the maximum magnitude of the sum of two vectors.
We'll call the two vectors
If we perform the addition
the result is a vector with magnitude
This represents the lowest possible magnitude of the sum of two vectors (magnitudes cannot be negative quantities). We therefore can expect the maximum magnitude to be if they are added together on the same axis (we'll say is the
If they are added along the same axis, the magnitude of the resultant vector is
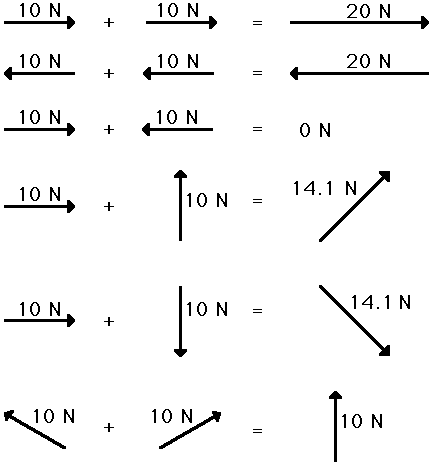
Here is a great visual about vector sum magnitudes (the vectors in this case are forces measured in newtons,