What is the concept of intron/exon?
1 Answer
A stretch of genetic DNA in eukaryote, stores the recipe of a polypeptide i.e. the sequence of amino acids present in the polypeptide is written in genetic code within the DNA.
An eukaryotic gene may possess some intervening sequences which are not supposed to be a part of actual coding sequence of RNA. The intervening sequences or introns are interspersed with actual coding sequences or exons within eukaryotic gene (=split gene).
When such an eukaryotic gene is transcripted, the RNA produced will possess both introns and exons. Intron sequences will be spliced off in posttranscriptional modification process and exons will join together to form a functional RNA molecule.
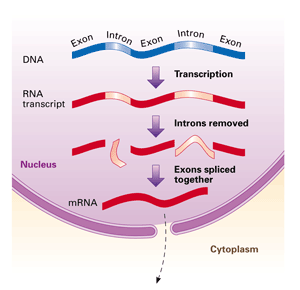
The differences between intron and exon could be enlisted as follows:
- intron sequence will be transcripted but not translated while exon sequence will be transcripted and translated, both.
- meaningful genetic codes are present in exons, not in introns.
- after transcription, intron parts are removed but exons are not.
- only exons become part of the functional RNA, introns fail to do so.
- a mutation in exon of gene may adversely affect the protein the gene codes for; a mutation in intron will not affect the protein in any way.
