Question #4977c
1 Answer
How about this?
Explanation:
Starting materials
The name itself gives you a clue.
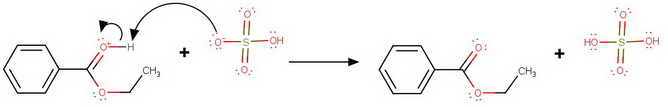
Ethyl phenylacetate is an ester of an alcohol and an acid.
The first word in the name tells you the alcohol is ethyl alcohol or ethanol.
The second word in the name tells you that the acid is phenylacetic acid.
So, the equation for the overall reaction is
The mechanism
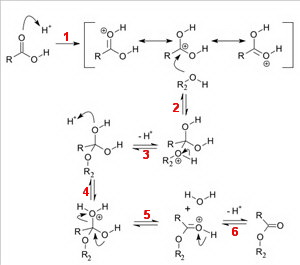
(Adapted from Diman Regional Vocational Technical High School)
Step 1. Protonation
Sulfuric acid protonates the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group to generate a resonance-stabilized carbocation with a more electrophilic carbon atom.
Step 2. Nucleophilic attack
The oxygen atom in ethanol attacks the carbocation.
Step 3 Deprotonation
The
Step 4. Reprotonation
… and replaces it on one of the
Step 5. Loss of water
A water molecule leaves, generating a protonated carbonyl group.
Step 6. Deprotonation
Finally, an
Here's an expanded version of Step 6.