A 2.3 kg steel ball strikes a wall with a speed of 8.5 m/s at an angle of 64⁰ with the surface. It bounces off with the same speed and angle. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.448 s. What is the average force exerted by the ball?
1 Answer
Explanation:
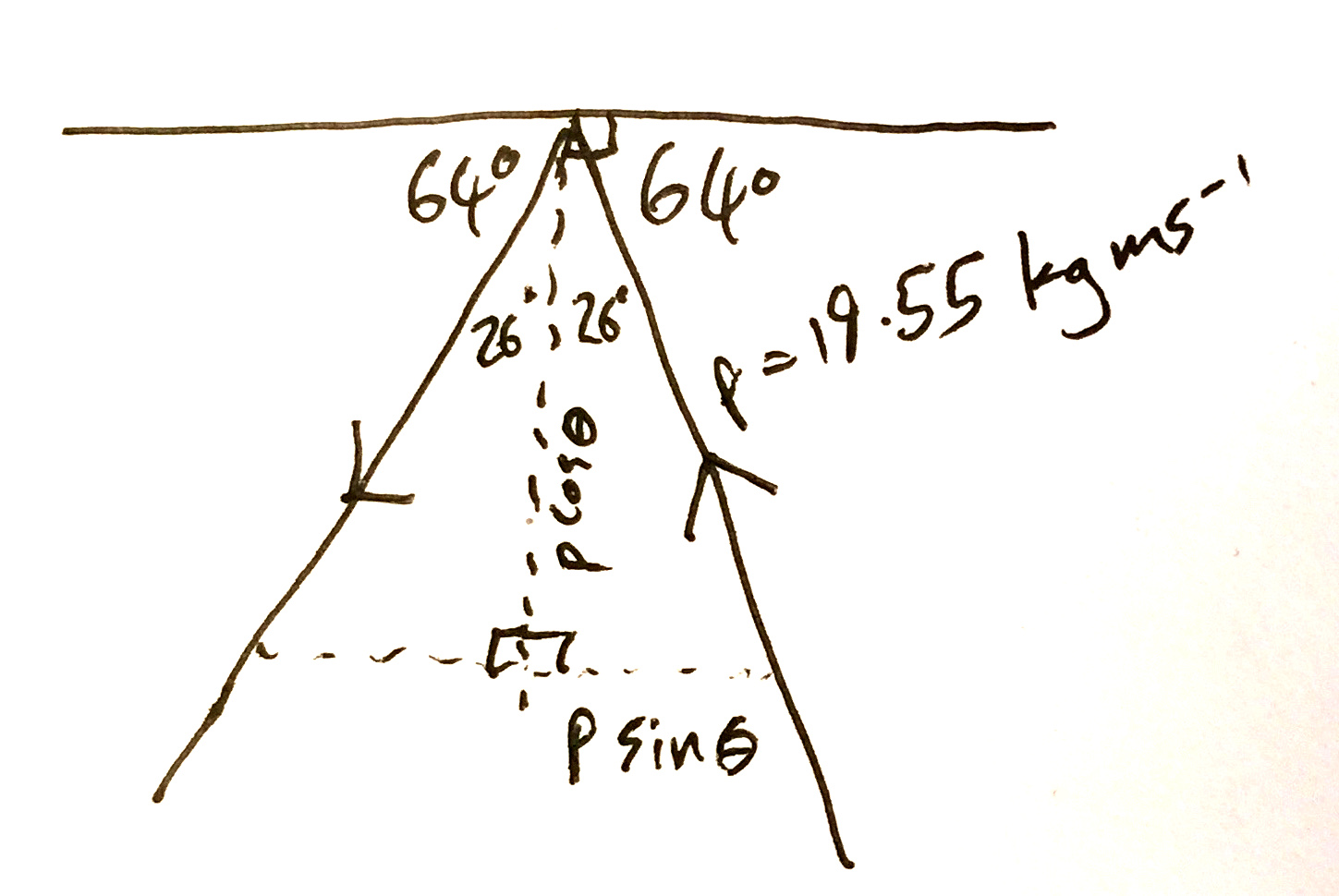
We know that the momentum before the collision would be the same as after it because of the conservation of momentum. This just means, though, that the change in momentum of the ball is matched by an equal change in momentum of the wall.
The impulse, and therefore the force, will be determined by the change in the momentum of the ball.
Due to the angle, though, the component of the momentum parallel to the wall will remain constant, while the component perpendicular to the wall will have its direction changed. We need to calculate the components.
Momentum of the ball:
Component of the momentum parallel to the wall:
Component of the momentum perpendicular to the wall:
The parallel component will be unchanged. If we choose 'toward the wall' as the positive direction, then the perpendicular component will change from
Impulse is equal to the change in momentum, and is defined by this equation:
Rearranging:

