At this instant, find the radial acceleration?

1 Answer
Feb 28, 2018
See the direction of acceleration shown in the picture of this question,shows the direction of net acceleration,which can be represented as the vector sum of tangential and radial acceleration.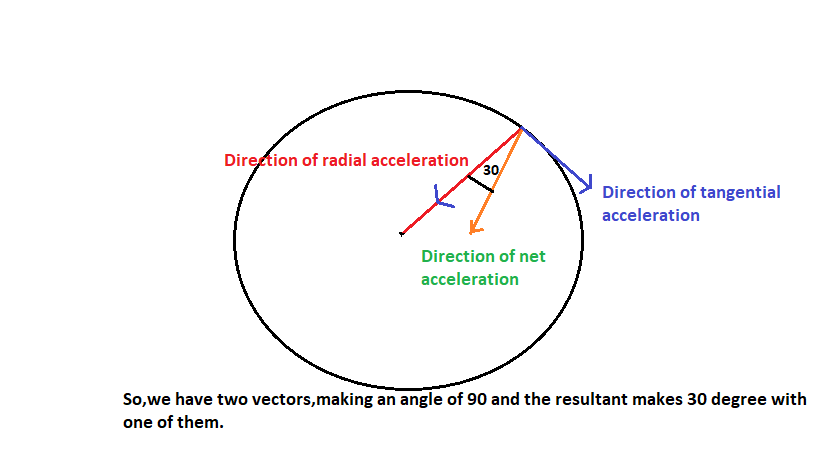
Now,we know,radial acceleration at any point =
So,we can write,
And,
Given,
so, our two equations become,
and,
Solving both,we get,
And,
So, radial acceleration =

