Briefly, explain the effect of pregnancy on the menstrual cycle?
1 Answer
Jul 19, 2017
Menstrual cycle remains arrested during pregnancy.
Explanation:
-
Menstrual cycle is generally repeated after every 28 days in women of reproductive age. The cycle has distinct preovulatory and postovulatory stages.
-
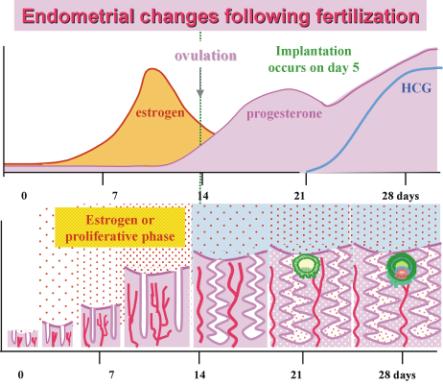
Oestrogen hormone is secreted from the surrounding tissue of a growing ovarian follicle in preovulatory stage under the influence of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) of anterior pituitary. Oestrogen helps in thickening of uterine lining by cell proliferation.
- Rising oestrogen level in blood provides positive feedback for secretion of anther pituitary hormone, namely luteinising hormone (LH).
- LH leads to bursting of the largest and mature ovarian follicle, disrupting tissues surrounding the follicle. This will:
I) cause drastic lowering of oestrogen level
II) lead to deposition of egg in fallopian tube
III) give rise to an endocrinal structure from empty follicle
- The new endocrinal structure is called corpus luteum (CL). As ovulation is over, the cycle has now entered post ovulatory stage and CL now starts secreting progesteron.
- Progesteron helps in maintaining the already thickened uterine lining for a possible implantation of fertilised egg.
- Pregnancy is possible when female's egg gets fertilised by male's sperms. If fertilisation takes place then there will be implantation of the embryo in uterine lining (within seven days of fertilisation) and this will be beginning of pregnancy.
- Once implantation of early embryo takes place surrounding tissue of uterus will start releasing a hormone named Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG).
- HCG provides a positive feedback for corpus luteum of ovary. Thus progesterone secretion continues and as a result the uterine endometrium remains thickened to nurture the implanted embryo.
- Progesterone is very important for continuation of pregnancy. It is also providing a negative feedback to endocrine system that blocks secretion of FSH. This will cause--
I) no further development of ovarian follicle
II) hence oestrogen level remains low
II) so release of LH and ovulation prevented

( )
)
- Maintenance of uterine lining to safe guard a growing embryo means menstrual bleeding will not take place throughout the pregnancy.
