Calculate N-Z ratio for Xe-135 and predict the type of decay it will undergo?
I understand how to get the ratio, which is 1.5. However, how do I predict the type of decay?
I understand how to get the ratio, which is 1.5. However, how do I predict the type of decay?
1 Answer
The
Explanation:
Thus,
Nuclei have a Belt of Stability, that is, a range of
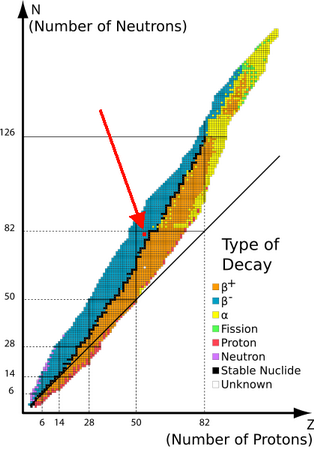
(Adapted from ... http://www.kentchemistry.com/links/Nuclear/BandStability.)
The red dot on the diagram above shows the position of
The range of stability for xenon nuclei is 1.30 to 1.48. The value of 1.50 for
A high
A neutron spontaneously changes to a proton and emits an electron (a β particle).
Thus the nucleus undergoes β-decay.
The equation for the transformation is

