Toluene and benzene have vapour pressures at 20 °C of approximately 22 mmHg and 75 mmHg, respectively. Calculate the total pressure of an ideal solution made up of 0.828 mol toluene and 0.172 mol benzene at this temperature?
1 Answer
The total pressure is 31 mmHg.
Explanation:
To solve this problem, we use Raoult's Law:
In symbols, the partial vapour pressure
#color(blue)(bar(ul(|color(white)(a/a)p_text(A) = chi_text(A)p_text(A)^@color(white)(a/a)|)))" "#
where
If we have two volatile components A and B, the total pressure
#p_text(tot) = chi_text(A)p_text(A)^@ + chi_text(B)p_text(B)^@#
Step 1. Calculate the mole fractions of
Let A = toluene and B = benzene. Then
Step 2. Calculate the total pressure
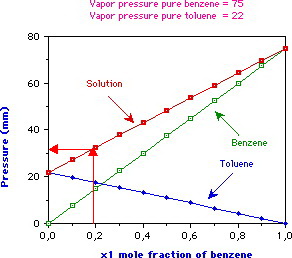
(Adapted from wpage.unina.it)
In the diagram above, you would start at just under 0.2 on the horizontal axis and go up until you hit the line for total pressure.
Then, you would draw a horizontal line to the left until you hit the vertical axis and find a total pressure of about 31 mmHg.

