How do enzymes speed up the chemical reactions? Use activation energy in your answer.
1 Answer
Just as catalysts do i.e by lowering the activation energy.
Explanation:
Enzymes are biomolecules
What they do is: They reduce the energy which reactants need to overcome energy barrier and to start a specific reaction. And this energy is called activation energy. They simply lower this energy, reducing the time for the reactants(substrates) to be transformed into products. Hence, Enzymes increase the rate of a specific biochemical reaction.
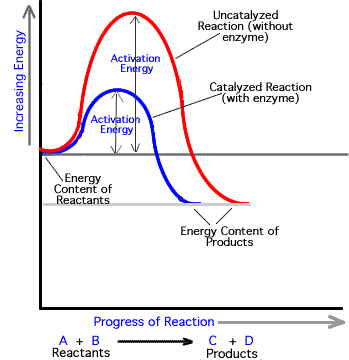
Example:
Hydrolysis of sucrose
Sucrase is a brush border enzyme of small intestine. During digestion in small intestine it hydrolyzes its specific substrate i.e sucrose. Sucrose is a diasscharide of glucose & fructose. Sucrose binds to sucrase at it's active site. Sucrase speeding up the hydrolysis, break the bonds b/w sucrose releasing fructose and glucose subunits.
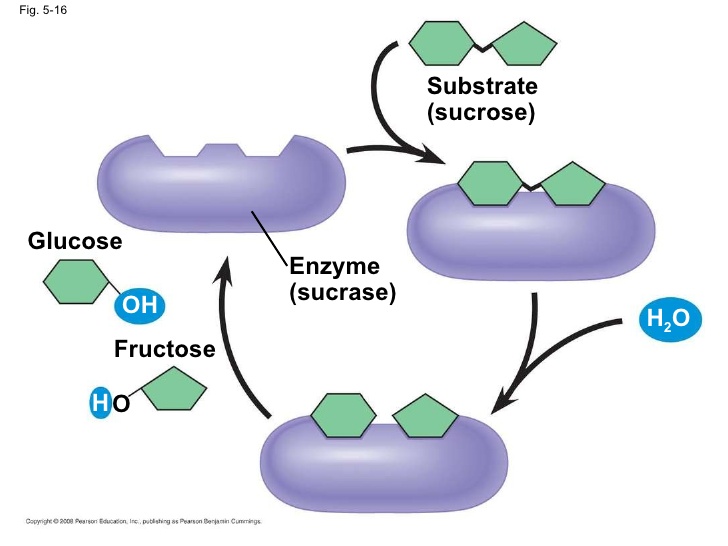
We can say that activation energy is the energy that is needed to destabilize the bonds b/w substrate molecule(s).
Hope it helps...

