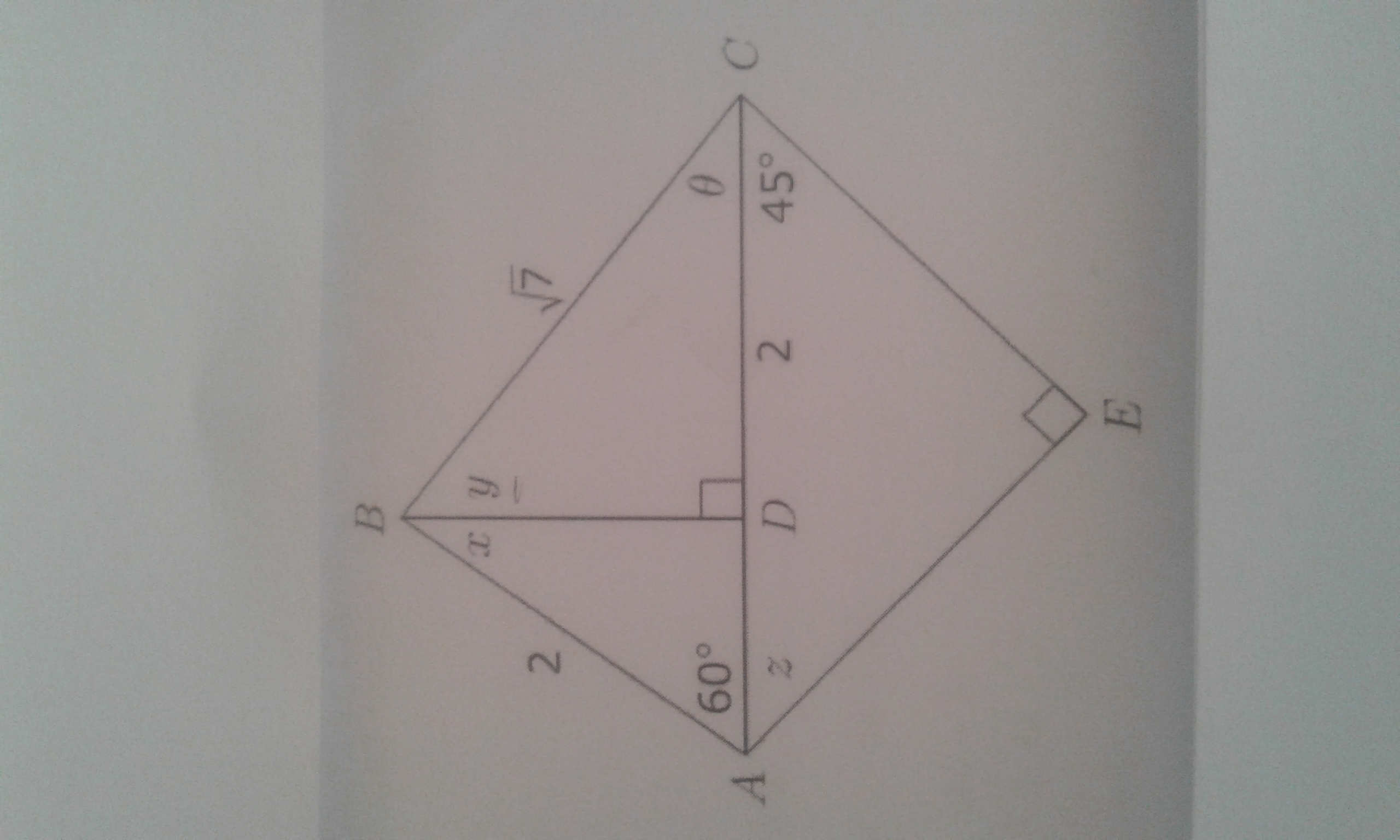
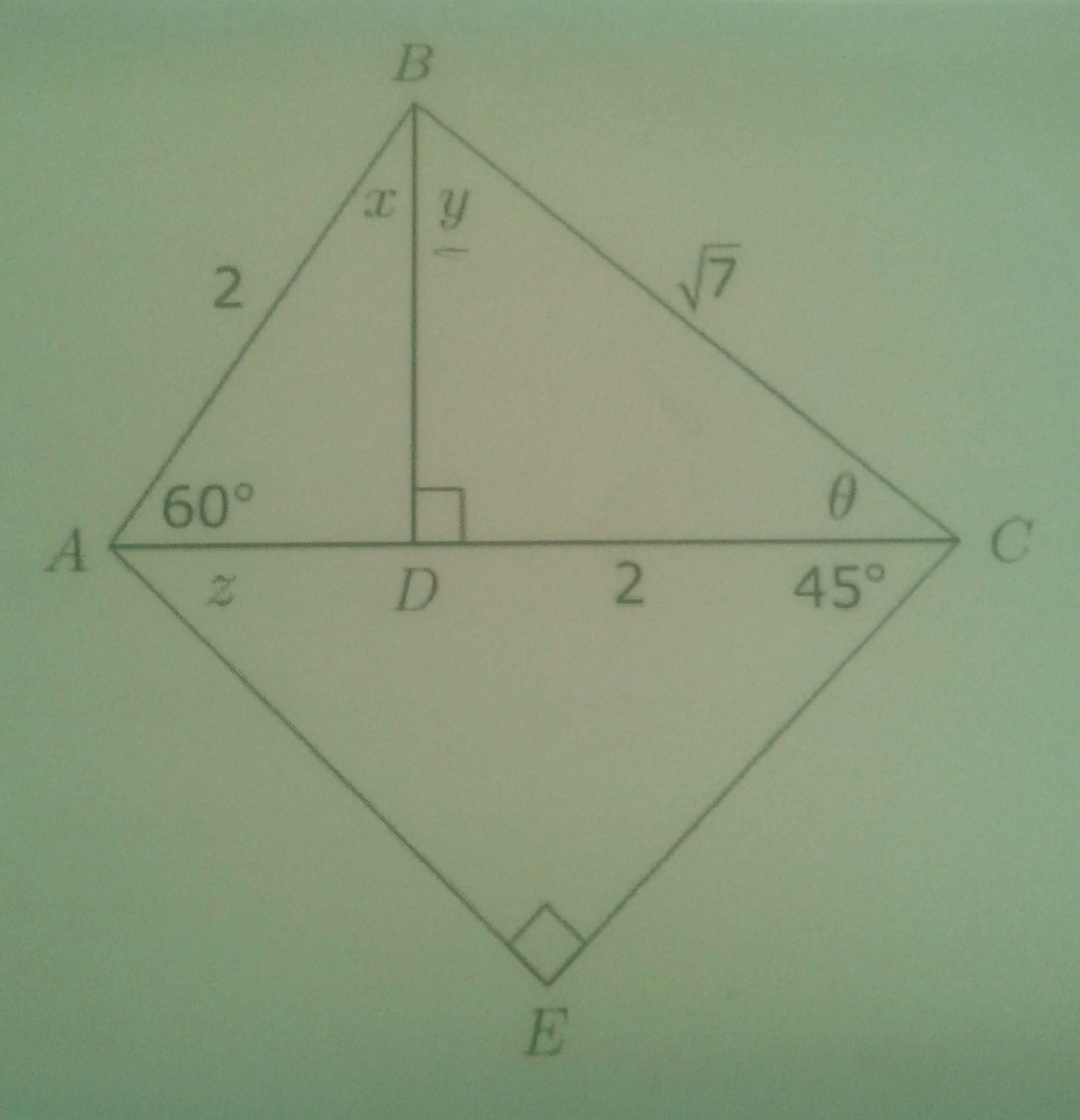
How do you determine the following? 1. cos 0 2. the length of BD 3. Determine y correct to 2 decimal places 4. calculate the length of EC with out a calculator?
1 Answer
See below
Explanation:
1
Using triangle DBC
2
Using triangle ABD:
3
Using triangle DBC:
4
First we can find the the length of AC. This will then be the hypotenuse of triangle ACE. We know DC=2. so we need to find AD.
Using triangle ABD:
So AC = AD + DC =
Looking at triangle ACE.
This means that:
AE = EC.
Letting
By Pythagoras's theorem:
Taking square roots:

