How much kinetic energy is lost in the collision? (See full question below)
A snooker ball, having a mass of #0.04# kg and initially moving with a speed of
#2ms^-1# strikes a stationary ball of the same mass. After the collision, the two balls are both moving with equal speeds at equal angles of #30°# to the original direction of the incident ball. How much kinetic energy is lost in the collision?
A snooker ball, having a mass of
1 Answer
0.026J
Explanation:
Start with a diagram.
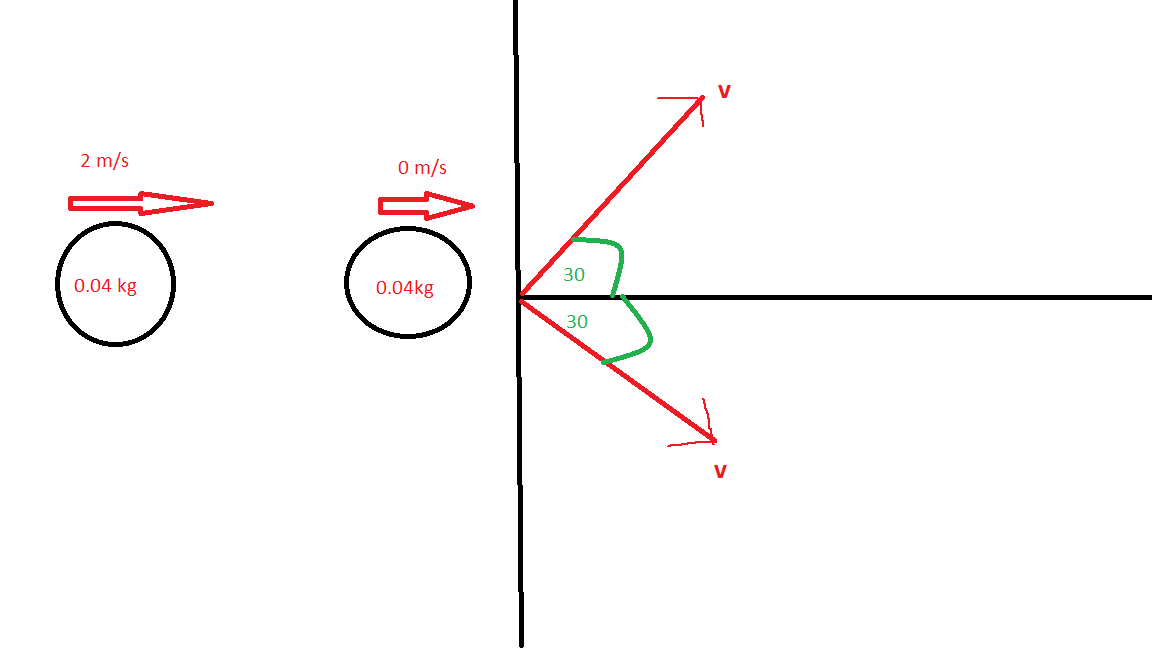
We need to find the final speed of the balls; let this be
By the conservation of momentum
Momentum before = momentum after
Now we can work out the kinetic energies.
