How to find the x-coordinates?

2 Answers
Please see below.
Explanation:
.
We take the first derivative of the function, set it equal to
These are the
We take the second derivative of the function, set it equal to
for
we have
You can see all this clearly in the graph of the family of functions for
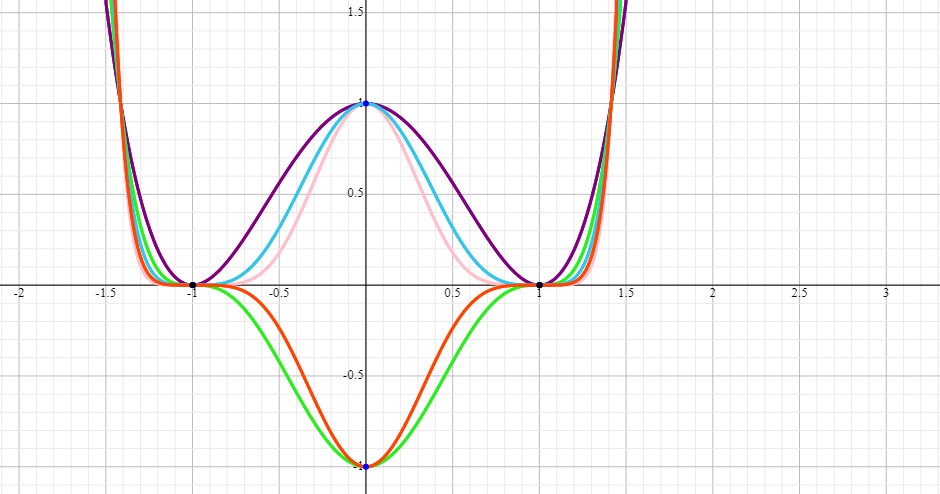
Explanation:
.

Geish,
If we calculate the right hand side of the matrix equation and set it equal to the left hand side which is the transformation matrix we find the following transformation:
This means in that if we plug these values in the
Let's solve for
For the two sides to be equal, we should have the numerators to be equal and the denominators to be equal:

