If I place a saltwater plant into a container of fresh water, the cells of the plant will absorb or release water?
1 Answer
Absorb
Explanation:
Typically the cells of aquatic plants are isotonic with their surrounding environment; i.e. the concentration of solute is equal between the cytosol and surrounding medium. In the case of saltwater/marine plants, the solute concentration within the cytosol of cells will be relatively higher than in freshwater, since saltwater has a higher concentration of solutes (mainly dissolved salts) than freshwater.
When placing a saltwater plant into a container of freshwater, the cells are thus introduced to a hypotonic environment, i.e. the concentration of solute is lower in the external medium than within the cell's cytosol. This establishes a concentration gradient by which water will be drawn into the cells by osmosis, since less water is within the cells than in the external environment.
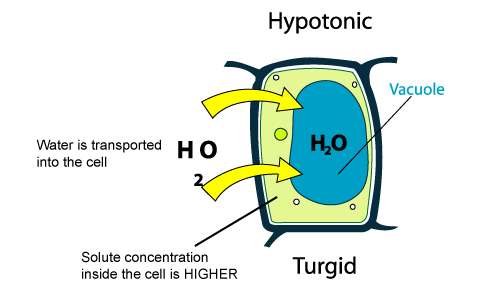
As shown in the diagram above, as water flows in, the cell will become turgid; the cell membrane is pushed against the cell wall due to the influx of water.

