If neurons in the central nervous system lack centrioles and are unable to divide, how do brain tumors develop?
1 Answer
Quick answer: No one really knows for sure.
Explanation:
What is a brain tumour?
A brain tumour is an abnormal growth of tissue in the brain that can disrupt proper brain function.
There are over 120 types of brain tumours, so I shall limit this discussion to the most common type: the astrocytomas.
An astrocytoma (Greek astron = "star" + kytos = "cell" + -oma = "tumour") is a tumour named after astrocytes, the star-shaped cells from which they grow.

Other supportive cells of the brain include oligodendrocytes (Greek oligo = "a few " dendron = "tree") and ependymal (Greek ependyma = "an upper garment") cells.
Collectively, these cells are known as glial (Greek glia = "glue") cells.
Tumours that arise from the glial tissue, which occupies half the volume of the brain, are called gliomas.
The most common and the most aggressive astrocytomas are glioblastomas (Greek blastos = "germ").
Their characteristic feature is necrosis (Greek necrosis = death) of the cells and proliferation of blood vessels around the tumor.
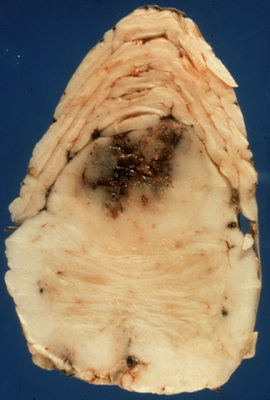
(from neuropathology-web.org)
Approximately 50% of astrocytomas are glioblastomas.
They are difficult to treat, and few patients survive much beyond 17 weeks without treatment.
Causes of gliomas
The cause of most gliomas is not known, and this is an active area of research.
Researchers speculate that genetic and immunologic abnormalities, exposure to ultraviolet rays, certain chemicals, ionizing radiation, diet, and stress may play contributing roles.

