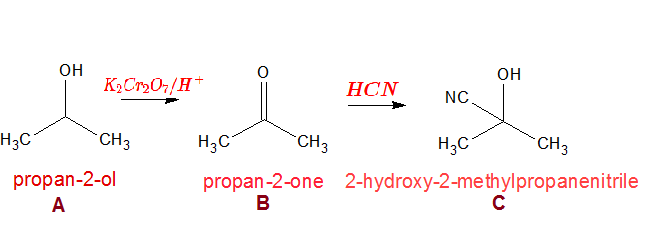
A compound A with a molecular formula C3H8O is oxidised with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) to form a liquid B. B reacts with hydrogen cyanide to form a compound C that contains 3 carbon atoms. What are the structures of A B and C?
2 Answers
Well, this is what I have... If
Likely the intention is the secondary alcohol for
There are three isomers of
"H"_3"C"-"O"-"CH"_2"CH"_3 "H"_3"C"-("CH"_2)_2-"OH" "H"_3"C"-("C"-"OH")-"CH"_3

The ether does not react with
In reacting with
That, however, should not happen with carboxylic acids. I showed the intermediate to hopefully make it clear.
It looks like
Considering that the final product
The starting material
It follows general molecular formula
The possible structural formula of saturated alcohols having molecular formula
(1)
and
(2)
For compound (1)
(1)
For compound (2)
(2)