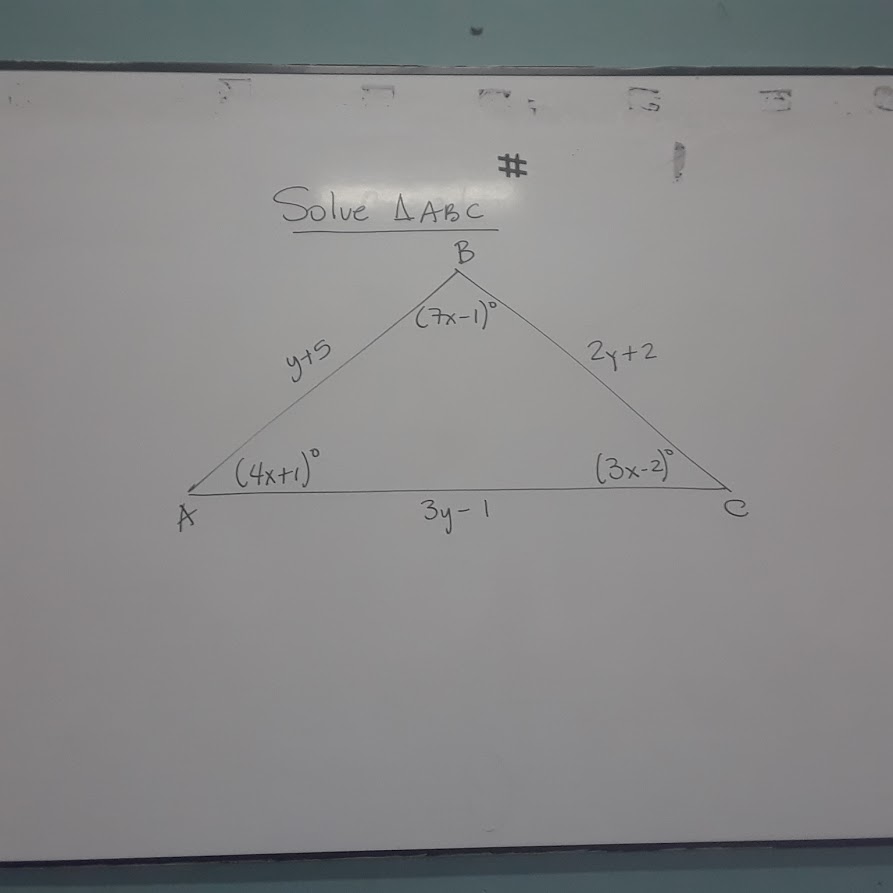
#" "#
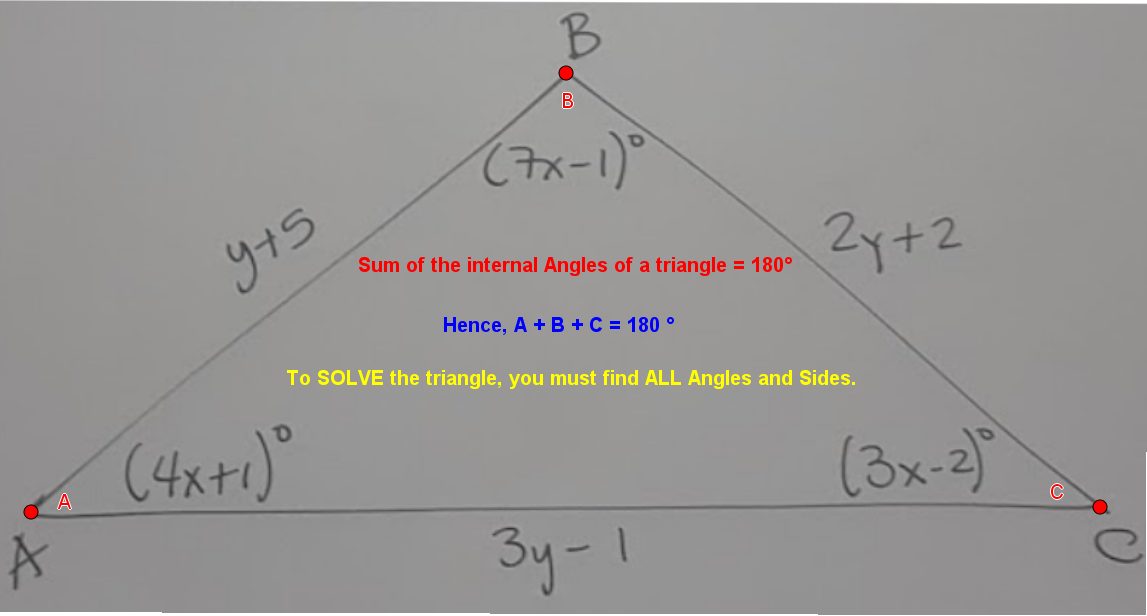
Sum of the internal angles of a triangle add to #color(blue)(180^@#
#color(green)("Step 1")#
Hence,
#(4x+1)^@ + (7x-1)^@ + (3x-2)^@ = 180^@#
#4x+1+7x-1+3x-2 = 180#
Combine the like terms:
#(4x+7x+3x)+cancel 1-cancel1-2=180#
#14x+cancel 1-cancel1-2=180#
#14x-2=180#
Add 2 to both sides of the equation.
#14x-cancel 2+cancel 2=180+2#
#14x=182#
Divide both sides of the equation by #14.#
#(14x)/14=182/14#
#(cancel 14x)/cancel14=cancel 182^color(red)(13)/cancel 14#
Hence #color(blue)(x = 13#
Substitute #color(blue)(x = 13# in
#color(green)((4x+1)^@ + (7x-1)^@ + (3x-2)^@ = 180^@# to obtain angles #A, B, C#
#A=[4(13)+1)]^@=(52+1)^@ = 53^@#
#B=[7(13)-1)]^@=(91-1)^@ = 90^@#
#C=[3(13)-2)]^@=(39-2)^@ = 37^@#
Hence, the angles are: #color(red)(A= 53^@, B= 90^@, C=37^@#, triangle #ABC# is a right-triangle.
#color(green)("Step 2")#
We have,
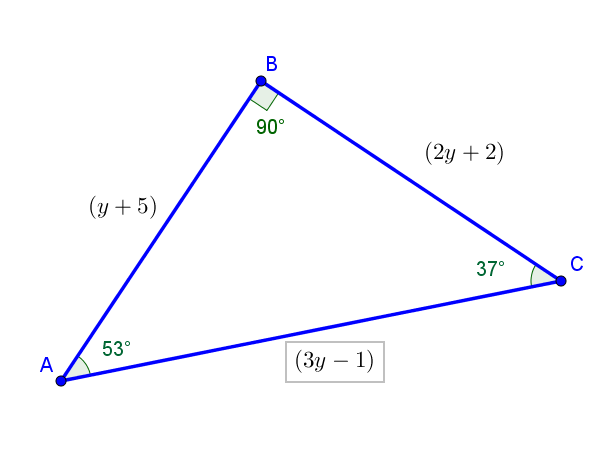
Since, #color(blue)("Angle B = 90"^@#, we can use the Pythagoras Theorem to find the magnitudes.
#AC# is the Hypotenuse, as it is the opposite side of #B#.
Hence,
#AC^2=AB^2+BC^2#
#(3y-1)^2 = (y+5)^2+(2y+2)^2" "# #[1]#
Use the Identities:
#(a+b)^2 -= a^2+2ab+b^2#
#(a-b)^2 -= a^2-2ab+b^2#
#[1]# becomes
#(9y^2-6y+1)=(y^2+10y+25)+(4y^2+8y+4)#
#9y^2-6y+1=y^2+10y+25+4y^2+8y+4#
Combine like terms:
#9y^2-y^2-4y^2-6y-10y-8y+1-25-4=0#
#4y^2-24y-28=0#
Divide both sides by 4.
#(cancel 4y^2)/cancel 4-(cancel 24^color(red)(6)y)/cancel 4-cancel 28^color(red)(7)/cancel 4=0#
#y^2-6y-7=0#
#y^2-7y+1y-7=0#
#y(y-7)+1(y-7)=0#
#(y-7)(y+1)=0#
#y=7, y=-1#
Ignore #y=-1#, as it would make the side #2y+2=0#
Consider #y=7.#
#AB=y+5=7+5=12#
#BC=2y+2=2*7+2=16#
#AC=3y-1=3*7-1=20#
Results:
#/_BAC = 53^@, /_ABC=90^@ and /_ACB=37^@#
#bar(AB)="12 Units", bar(BC) = "16 Units", bar(AC)= "20 Units"#