Using Hess' Law, how do you calculate the standard heat of formation of Copper(I) Oxide given the following data?
#CuO(s) -> Cu(s)+ 1/2 O_2 # # Delta H = 157.3 kJ# #/# #mol#
#4CuO(s) -> 2Cu_2O(s) + O_2(g)# #Delta H 292.0 kJ# #/# #mol#
1 Answer
You can do it like this:
Explanation:
Hess' Law states that the overall enthalpy change of a process is independent of the route taken.
In thermodynamics we are interested in initial and final states.
You need to construct a Hess Cycle using the information given:
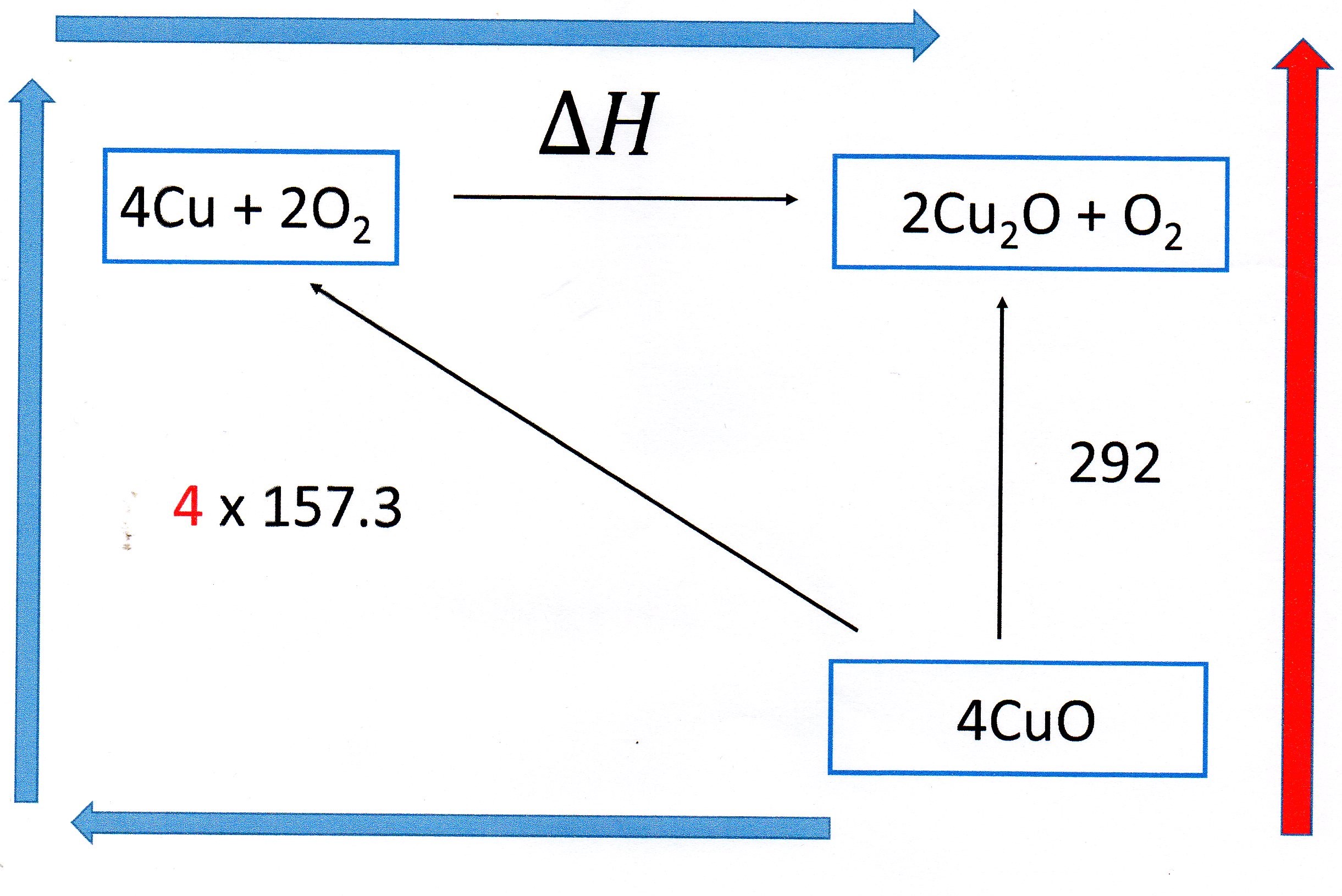
You can see that, in energy terms, the
So we can write:
Enthalpy of formation refers to the formation of 1 mole of a substance from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions.
We have found
Which is the same as:
This refers to the formation of 2 moles of copper(I) oxide. We need the enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mole of copper(I) oxide.

