What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell?
1 Answer
See below!
Explanation:
Here are some major differences b/w prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.
-
Eu mean true
& karyon mean nucleus. Hence, eukaryotes are the one which have true nucleus.
Pro mean before& karyon mean nucleus. So, prokaryote mean before or without any true nucleus. -
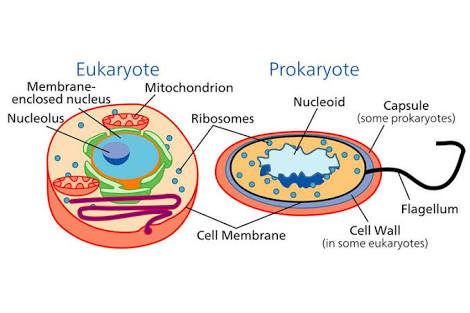
Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bounded organelles. While eukaryotes have several membrane-bounded organelles I.e Mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, peroxisomes, lysosomes etc.
-
All prokaryotic cells have peptidoglycan cell wall. Some eukaryotee e.g plant & fungi contain cell wall. Plants contain cellulose cell wall
& fungi contain chitin cell wall. -
Prokaryotes have smaller ribosome of
"70 Svedberg" while eukaryotes have a larger one"80 Svedberg" . -
In prokaryotes, site for both transcription & translation is cytoplasm(as they don't have nucleus). But in eukaryotes, transcription take place within nucleus and translation within cytoplasm.
-
In prokaryotes, all the steps of cellular respiration takes place within cytosol. In eukaryotes: glycolysis takes place within cytosol, Krebs cycle within mitochondrial matrix &
"ETC" within inner mitochondrial membrane. -
Prokaryotes undergo binary fission(only cytokinesis) & conjugation. Eukaryotee perform mitosis, meiosis(both karyokinesis and cytokinesis).
-
Prokaryotic cells have large single chromosome which is wrapped up in a circular shape. Eukaryotee cells contain several pairs of chromosomes.
Hope it helps!

