What are the principle parts of a cell?
1 Answer
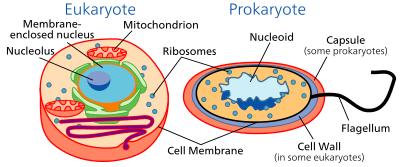
All cells have a Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm and Chromatin (genetic material)
Explanation:
No matter what type of cell, animal, plant, bacteria, all cells have a Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm and Chromatin (genetic material).
However there are many organelles that comprise the anatomical and physiological aspects of the cell.
Cell Membrane - Outer protective, selectively permeable boundary with the cell's environment.
Cell Wall (plant, fungi, bacteria) - Support mechanism and protective boundary of the cell.
Cytoplasm - Internal plasma structure housing all other cell organelles and providing cell shape.
Chromatin - Genetic material including DNA and RNA, providing the blueprint of cell structure and function for the production of proteins.
Nucleus (eukaryotic cell) - Nuclear membrane (envelope) surrounds the chromatin. Nucleolus oversees nuclear activities within the cell and nuclear.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (rough) - Pathway for the production of proteins containing Ribosomes to process amino acid chains.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (smooth) - Pathway for materials throughout the cell.
Mitochondria - Powerhouse of the cell producing energy (ATP) through cellular respiration.
Chloroplasts (plants, algae) - Produce stored energy through photosynthesis.
Vacuoles - Storage bubbles for food, energy and wastes.
Lysosomes - Digestive plastids for woods and wastes.
Chromoplasts (plants, algae) - Storage and processing of oils and pigments for energy production.
Cilia, Flagella, Pseudopods - External projections of the cell membrane for movement and food gathering.
These are all simplifications of the actual processes and functions of the organelles of a cell.
 4.bp.blogspot.com
4.bp.blogspot.com
Image from 4.bp.blogspot.com

