What compounds are derived from cholesterol?
2 Answers
Many compounds are derived from cholesterol.
The structure of cholesterol is shown below. The steroid skeleton is shown in red.

Many compounds are derived from cholesterol. Here are some examples.
BILE SALTS

Bile salts promote the absorption and absorption of dietary fat. Sodium glycocholate is an important bile salt.
STEROID HORMONES
-
Progestogens

Progesterone is responsible for preparing the body for pregnancy and maintaining it until birth. -
Glucocorticoids

Cortisol plays an important role in the metabolism of glucose. -
Mineralocorticoids

Aldosterone increases blood volume and blood pressure by increasing the reabsorption of Na⁺ and the excretion of K⁺ and H⁺ in the kidneys. -
Androgens
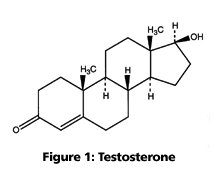
Testosterone is responsible for the development and maintenance of male secondary sex characteristics. -
Estrogens
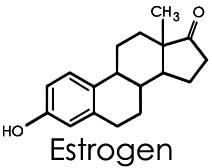
Estrogens are involved in the development and maintenance of female secondary sex characteristics.
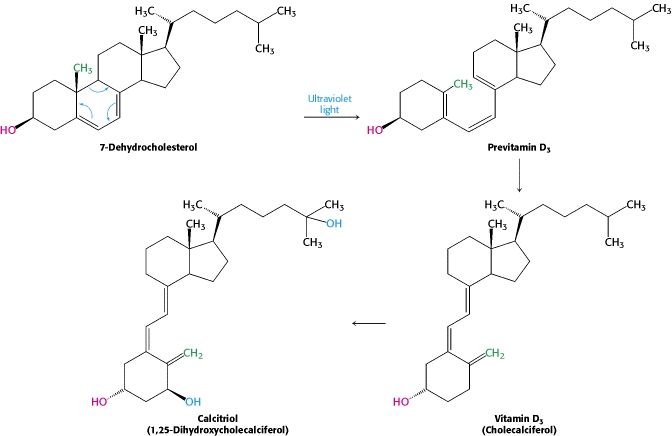
VITAMIN D

Vitamin D₂ is one of a group of cholesterol derivatives responsible for enhancing the intestinal absorption of calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphate, and zinc.
There are many compounds derived from cholesterol, including vitamin D, bile salts, and steroid hormones.
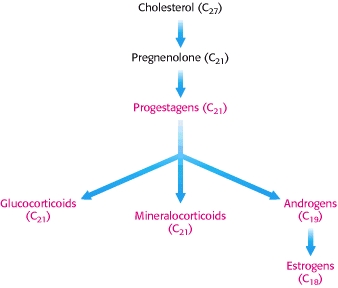
Cholesterol is the precursor of the five major classes of steroid hormones: progestagens, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22339/
Vitamin D Synthesis. The pathway for the conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol into vitamin D3 and then into calcitriol, the active hormone.
Biosynthetic Relations of Classes of Steroid Hormones and Cholesterol
For more information go to the following website: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22339/


