What is Le Chatelier's principle in chemistry?
1 Answer
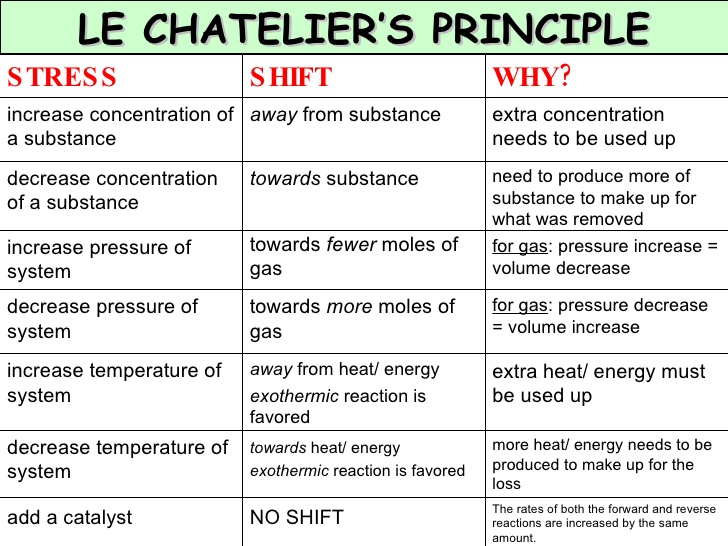
Le Chatelier's principle states that if a "stress" is placed on a system that is at equilibrium, the system will shift in such a way to relieve that stress.
Explanation:
The "stress" on a system can be attributed to:
- Changing the concentration of the reactants or products
- Altering the temperature of the system
- Changing the pressure of the system
Here's a brief overview, but I'll provide longer definitions and examples if you want to read it:
 https://www.pinterest.com/explore/le-chatelier's-principle/
https://www.pinterest.com/explore/le-chatelier's-principle/
I'll list explanations of each stress below, along with a few illustrations to make Le Chatelier's principle easier to understand.
Let's say you have this chemical reaction:
If you increase the concentration of one of the reactants, let's say
Now if you remove one of the products say,
 http://slideplayer.com/slide/2423137/
http://slideplayer.com/slide/2423137/
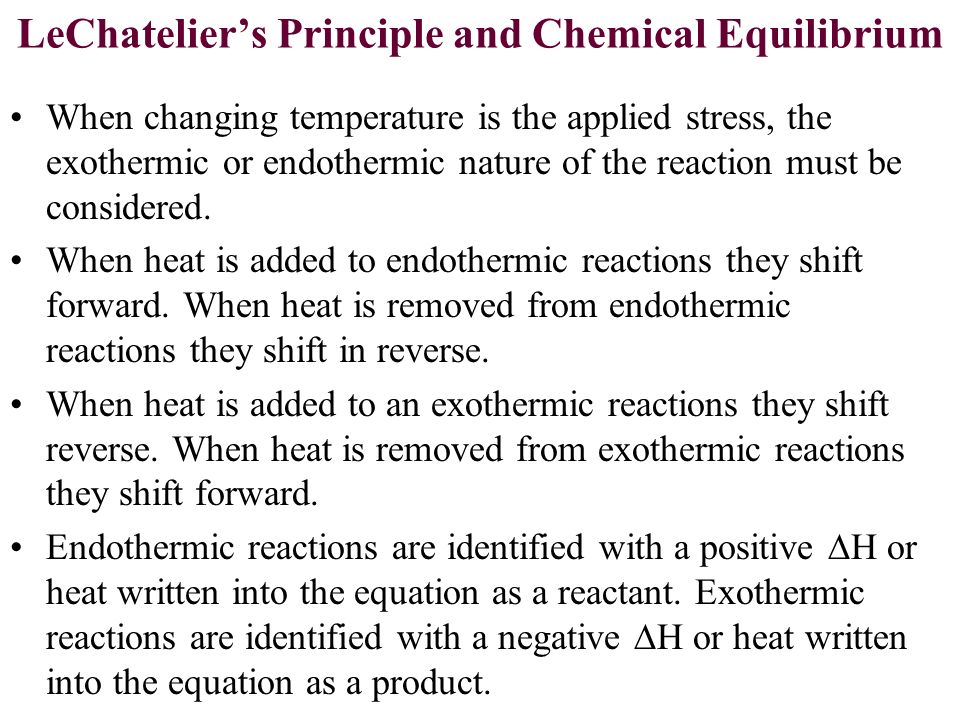
Let's use the same chemical reaction and assume that it is endothermic.
If the temperature is increased, the reaction will proceed from the reactants to the products. This is because you now have additional energy in the form of heat so the system wants to shift away from that extra heat and consume it in order to restore equilibrium.
Now, let's say that the chemical reaction happened to be exothermic.
If we decrease the temperature, the reaction will proceed towards the products because the system must regenerate the heat that was lost.
 http://slideplayer.com/slide/6382421/
http://slideplayer.com/slide/6382421/
Now, we'll use another chemical reaction:
If we increase the pressure of

