What is lymphatic system cancer?
1 Answer
Lymphoma
Explanation:
Lymphoma is the cancer of the lymphatic system.
To help you understand better, let's start with the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system, part of the immune system, is a system of thin tubes and lymph nodes that run throughout the body. There are groups of lymph nodes throughout the body including in the neck, armpits, groin, chest and abdomen. They are connected by a network of fine tubes called lymphatic vessels. Lymph nodes filter disease and germs from lymph, a liquid that travels through the lymphatic vessels.
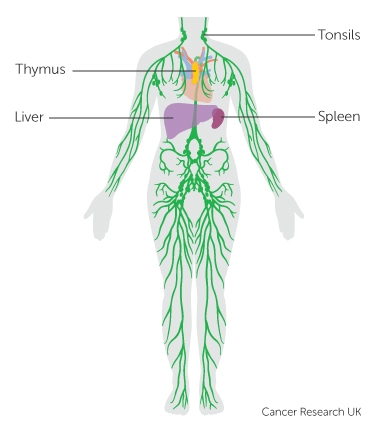
There are two main types of lymphoma: Hodgkin's lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. They can be differentiated by examination of the cancer cells under a microscope. Around 20% of all lymphoma diagnosed are Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Cancer occurs when normal cells undergo a transformation whereby they grow and multiply uncontrollably. Lymphoma is a malignant transformation of either B or T lymphocyte cells or their subtypes. Lymphoma, blood cells called lymphocytes become abnormal. These abnormal lymphoma cells keep dividing and grow out of the body’s control. Over time, the number of lymphoma cells increases and they form a lump called a tumor. The most common place for lymphoma to occur is in the lymph nodes. However, lymphoma can begin in almost any part of the body. Lymphoma that grows outside the lymph nodes is called extranodal lymphoma.
Because lymphocytes travel around the body, lymphoma can spread from where it first started. It can spread through the lymphatic system from lymph nodes in one part of the body to lymph nodes elsewhere. Lymphoma cells can also travel in the bloodstream to organs such as the bone marrow, liver or lungs. When the lymphoma cells reach a new area, they may carry on dividing and form a new tumor.
Read more: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancer-basics/lymph-nodes-and-cancer.html and https://www.macmillan.org.uk/information-and-support/lymphoma/

