What is polygenic inheritance?
2 Answers
Polygenic inheritance means a character which is controlled by more than two genes.
Explanation:
A character or an allele is specially controlled by 1 pair of a gene.Like in Mendel examination the height of pea plant is controlled by 1 pair of a gene. But there are some characters which are controlled more than one gene pair.For example, Human skin color. Its a perfect example of polygenic inheritance.Because it is controlled by 3pair of a gene. Nilson-Ehle first described the polygenic inheritance.Moreover human eye colour, 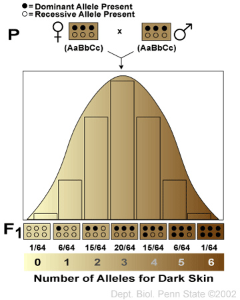 weight and height also an example of polygenic inheritance. That's all I know.Hope this help :)
weight and height also an example of polygenic inheritance. That's all I know.Hope this help :)
The inheritance mode of polygenic patterns is called polygenic inheritance.
Explanation:
Polygenic inheritance is also known as quantitative inheritance and refers to a single inherited phenotypic trait that is controlled by two or more different genes.
It refers to inheritance of a phenotypic characteristics (traits) that is attributable to two or more genes and can be measured quantitatively. Polygenic traits do not follow patterns of Mendelian inheritance. Instead, their phenotypes typically vary along a continuos gradient depicted by a bell curve. It occurs when one characteristic is controlled by two or more genes. Often the genes are large in quantity but small in effect.
Polygenic traits may display a range of possible phenotypes, determined by a number of different genes and the interactions between them. Polygenic traits exhibit incomplete dominance so the phenotype displayed in offsprings is a mixture of the phenotypes displayed in the parents. Each of the genes that contributes to a polygenic trait, has an equal influence and each of the alleles has an additive effect on the phenotypic outcome.
Due to the inheritance mode patterns, the physical traits that are controlled by polygenic inheritance, such as hair colour, height, and skin colour,as well as the non-visible traits such as blood pressure,intelligence, autism, and longevity, occur on a continuous gradient, with many variations of quantifiable increments.
Polygenes exist in other organisms too. Drosophila for instance display polygyny with traits such as wing morphology, bristle count and many others.


