What is the difference between an oxyacid and an organic acid? What are examples of each?
1 Answer
The difference lies in the structure of the molecules and the manner in which the oxygen and hydrogen atoms are arranged. See below...
Explanation:
An oxyacid is one that will contain, in addition to hydrogen and another element (such as nitrogen, sulfur or phosphorus), a number of oxygen atoms.
Examples would include sulfuric acid
An organic acid is one which contains, in its structure, the particular arrangement of atoms called a carboxyl group
Examples include formic acid
The difference comes in the actual structure of the molecule. In the oxyacid, the oxygen atoms are all bonded to the nitrogen or sulfur, or whatever it happens to be, with hydrogen atoms bonded to one or more of these oxygens.
In a carboxylic acid (the organic variety), a carbon is doubly bonded to one oxygen atom and singly bonded to a second oxygen. This second oxygen has the H atom bonded to it. So, a very particular structure.
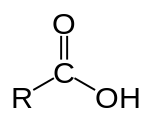
"R" just represents the rest of the molecule.

