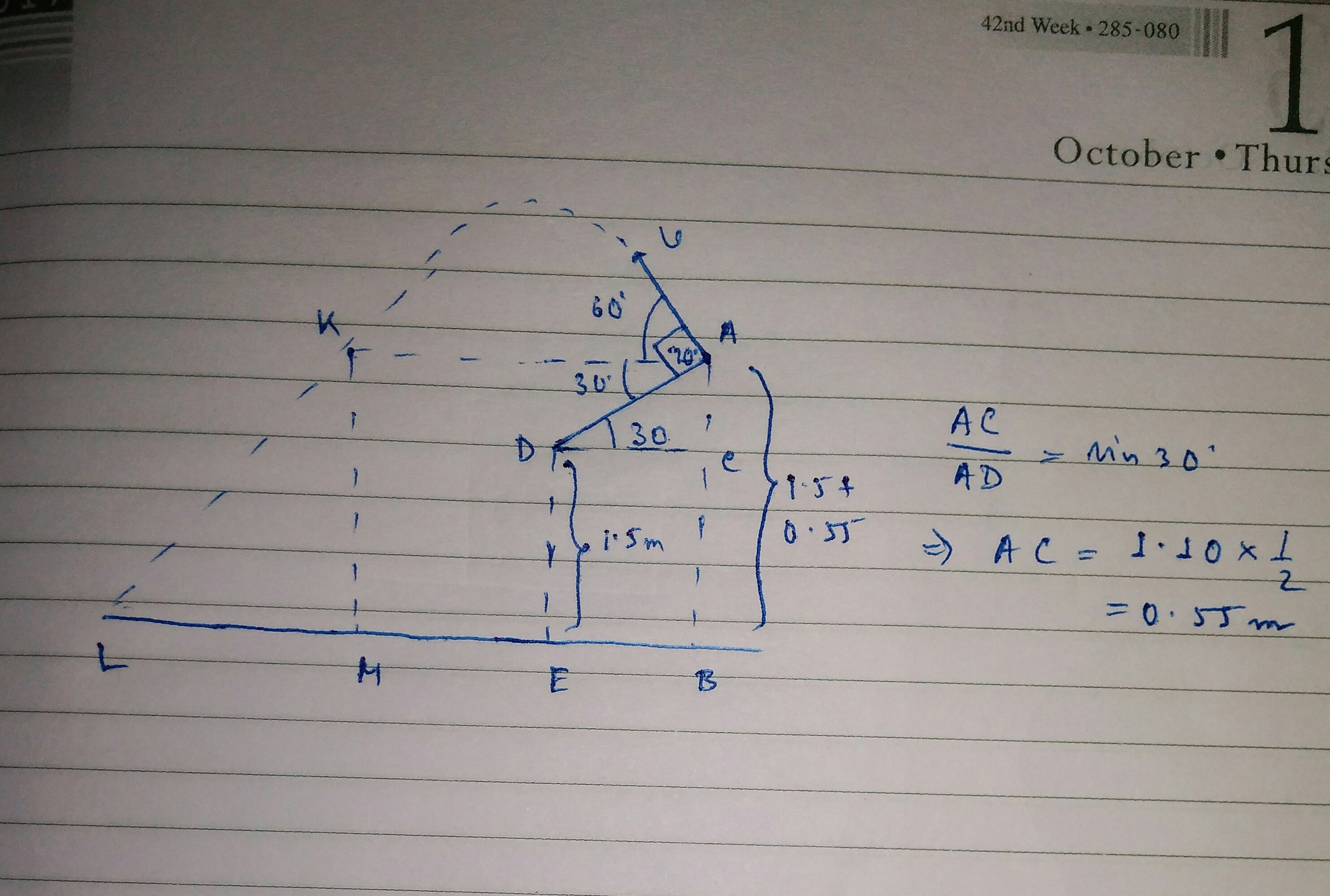
 So,we can calculate the length #AK=BM# from the the diagram,as the range of projectile motion,using the formula, #R= (u^2 sin 2 theta )/g = (1^2 sin 120)/g=0.087 m#
So,we can calculate the length #AK=BM# from the the diagram,as the range of projectile motion,using the formula, #R= (u^2 sin 2 theta )/g = (1^2 sin 120)/g=0.087 m#
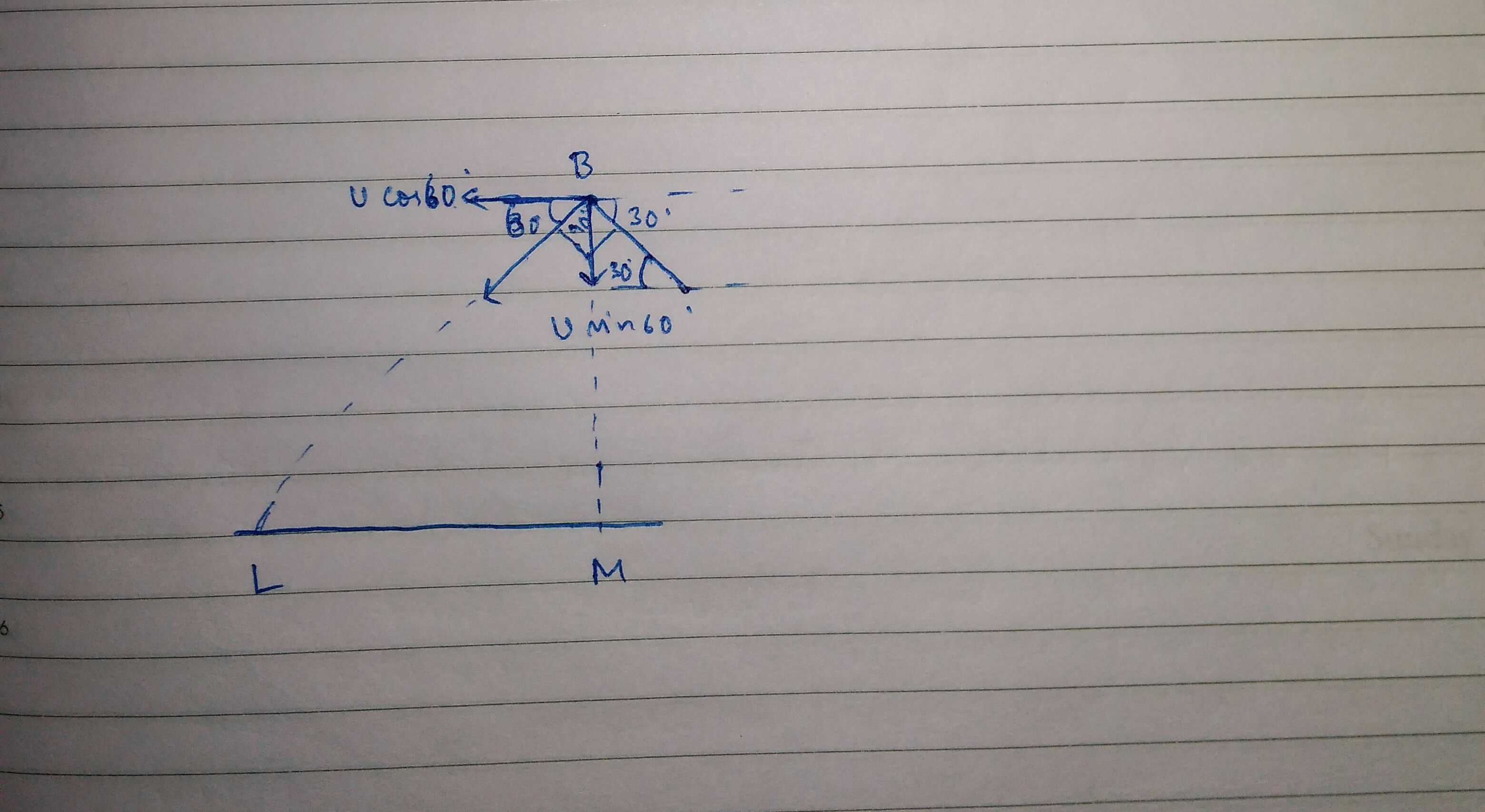
Now,when the stone will return to point #K# it will have the same vertical component of velocity that it had at point #A#,but it will be directed downwards,
So,at point #K# downward component of velocity = #v sin 60 = sqrt(3)/2#
Now,if it takes time #t# to reach the ground,then considering only vertical motion,we can write,
#2.05 = sqrt(3)/2 t + 1/2 g t^2# (using, #s= ut +1/2 g t^2#)
So, #t=0.55 s#
So,in that time if the stone horizontally went from #M# to #L#,then, #ML = v cos 60 *t= 1/2 *0.55=0.275 m# (using, #s=vt#, as horizontal component of velocity remains unchanged)
So,range of motion = #BM + ML = 0.087 + 0.275=0.362m#
Now,you can easily work out the 2nd part of the question, here your range will be only, #LM# of the 1st problem's picture.
Here is a diagram to help you,


 So,we can calculate the length
So,we can calculate the length 

