When can resonance structures be written for a molecule?
1 Answer
You can write resonance structures for any compound or ion that contains one or more double or triple bonds.
Explanation:
Whenever you can draw two or more structures for a substance that differ only in the location of the electrons, the actual structure is none of them.
Rather, the actual structure is a resonance hybrid of them all.
For example, we can write three equivalent structures for formaldehyde, differing only in the position of the electrons.
Admittedly, the charged structures are minor contributors, but they are contributors.
Resonance is more important when you can draw equivalent structures for a substance.
For example, you can draw three equivalent structures for the carbonate ion,
www.chem.ucla.edu
A well-known example of resonance is that of benzene.
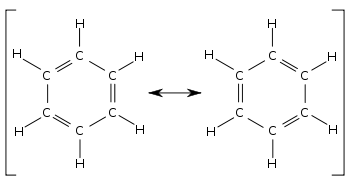 upload.wikimedia.org
upload.wikimedia.org
It has two equivalent structures that differ only in the position of the electrons.

