Explain the role of Van der Waals forces in pvc plastic?
1 Answer
The main van der Waals forces in PVC are dipole-induced dipole forces.
van der Waals forces include dipole-dipole, dipole-induced dipole, and London dispersion forces. The most important forces in PVC are dipole-induced dipole attractions.
PVC is a polymer of vinyl chloride.
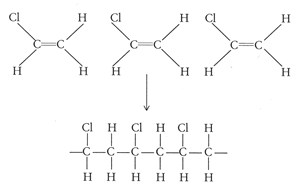
It is tempting to say that the molecules line up as in the diagram below. It looks as if are dipole-dipole forces between adjacent molecules
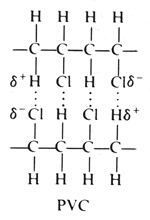
But the Cl atoms are large, and they stick out from the chain in random directions.

It is difficult for the chains to lie close together. Where the chains do come close, there are van der Waals attractions.
The C-Cl bond is polar, with a partial negative charge on the Cl atom.
The Cl atom is most likely to come close to an H atom in a nearby molecule.
The C-H bond in the adjacent molecule is nonpolar, so the H atom has no charge.
When the Cl atom approaches, the partial negative charge on the Cl repels the electron cloud on the H atom. This causes a partial positive charge on the H atom and induces a C-H dipole.
Each dipole-induced dipole interaction is not strong. But there are so many of them that pure PVC is a hard, brittle solid.
The PVC in ropes is flexible because it contains a plasticizer to soften it.

