Question #22228
1 Answer
You can calculate the frequency(
the speed of light(c)=frequency(
An important thing to know is that this is an algebraic equation, so we can solve for an individual piece by using our algebra rules; in this case to solve for frequency.
Our new equation would be:
Also since the speed of light is given in units of meters/second & the wavelength will be in nanometers, you will have to convert your wavelength to units of meters to get the correct units for frequency (1/second.)
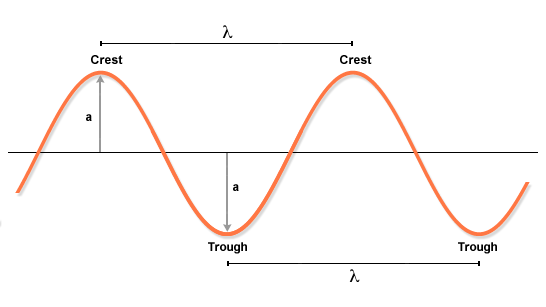
As electromagnetic radiation moves away from its source the positions of maximum and minimum amplitude-peaks and troughs-are regularly spaced.
The distance from peak-peak or from trough-trough is called the wavelength (
you can also use the same method as shown above to solve for

