How can I calculate thermochemistry equations for phase changes?
1 Answer
Phase changes represent the transformation of a thermodynamic system from one state of matter to another by way of heat transfer. A state of matter (or phase) is described as having uniform physical properties; during phase changes, certain properties change.
Now, heating stuff up takes energy; for a pure substance in a single phase, this energy can be calculated using the equation
However, this equation cannot be used for phase changes, since temperature does not change during a phase change,as you can see in this diagram depicting water's phase changes:
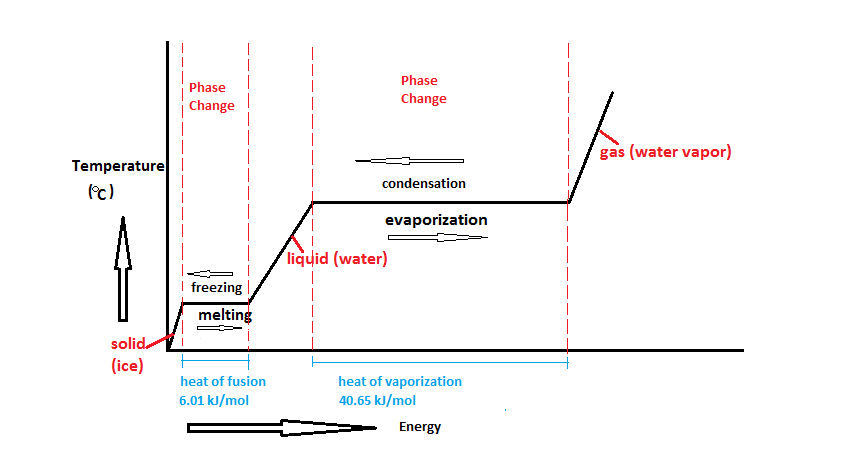
We know that the difference between any two phases is simply the energy difference, therefore all we need to know is that amount of energy to be able to calculate the heat involved. The equation used is
If you're going from solid to liquid, you use
If you're going from liquid to gas, you use
For water, the values are usually given to be
Therefore, all you need to know in order to determine the heat needed to go through a specific phase change is the substance's mass and the values for its heat of fusion and/or heat of vaporization.

