d/{dx}arccos({2x+1}/2)={-1}/{\sqrt{3/4-x-x^2}}
First I will prove a result needed to do the differentiation:
d/{du}arccos(u)={-1}/{\sqrt{1-u^2}}
Proof:
Let y=arccos(u), take the cosine of each side.
\impliescos(y)=u, now differentiate each side with respect to u
\implies -sin(y){dy}/{du}=1
\implies {dy}/{du}=d/{du}[arccosu]={-1}/{sin(y)}
Draw a triangle that agrees with the earlier expression, cos(y)=u to find out what sin(y) is equal to. From the diagram below, sin(y)=\sqrt{1-u^2}
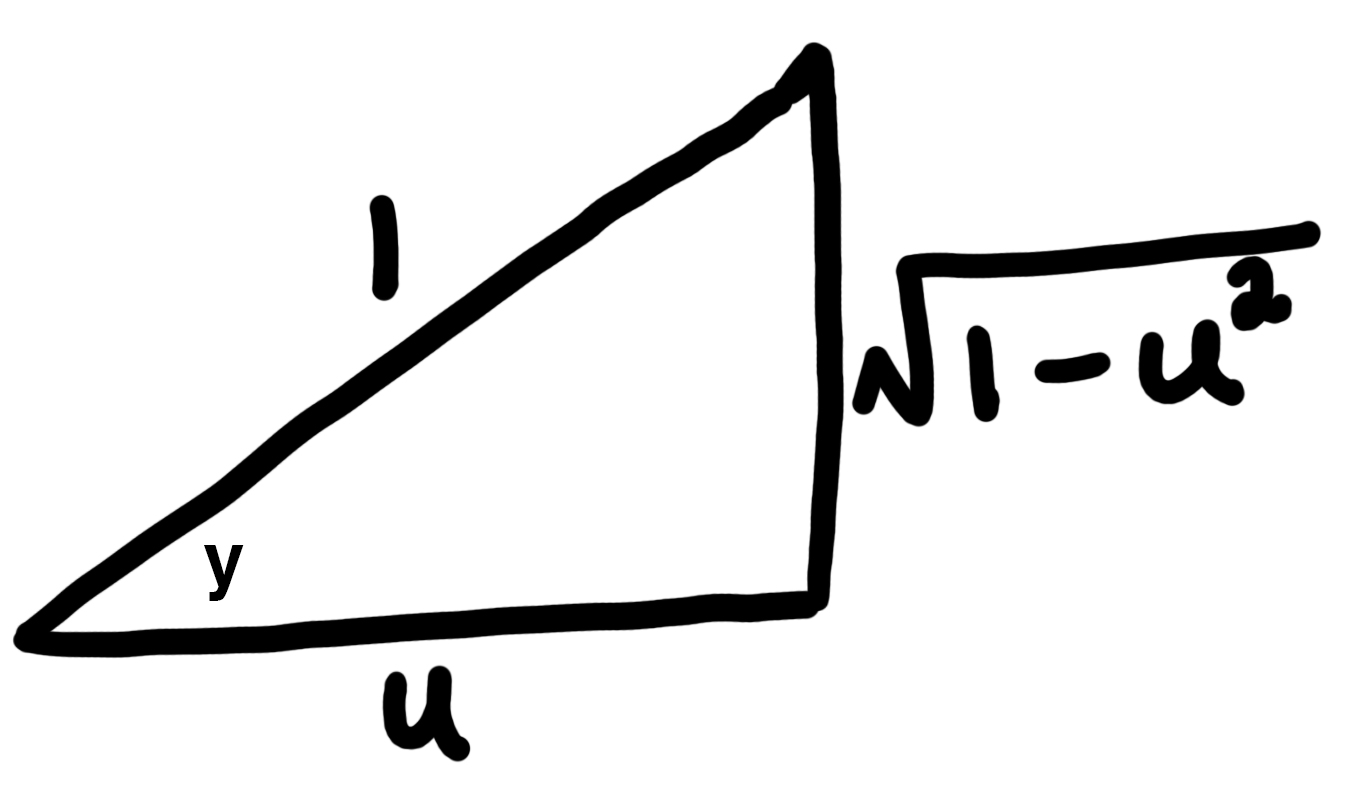
Substitute sin(y) to get the desired result:d/{du}arccos(u)={-1}/{\sqrt{1-u^2}}
Now use the chain rule to take the derivative of y=arccos({2x+1}/2)
Let u={2x+1}/2 so that y=arccos(u)
Chain Rule
d/{dx}y={dy}/{du}*{du}/{dx}=( {-1}/{ \sqrt{1-u^2} })(1)
Substitute u in the above result to get
d/{dx}arccos({2x+1}/2)={-1}/{\sqrt{3/4-x-x^2}}

