What happens to a protein or nucleic acid if it is denatured?
1 Answer
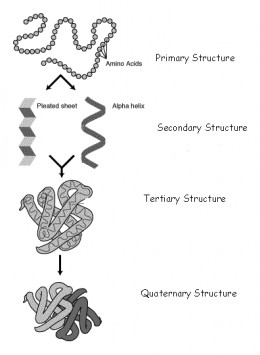
If a protein or nucleic acid is denatured, it loses its secondary or tertiary structure.
Explanation:
Denaturing changes the shape of a protein or nucleic acid although it does not change the primary amino acid sequence, also known as the primary structure. To break the primary structure, peptide bonds would need to be broken, and denaturing does not do this.
Denaturing can happen when a protein or nucleic acid is exposed to heat or chemicals such as ethanol, formaldehyde, sodium bicarbonate, and others.
Cooking food for example denatures some of the proteins in the food, making it easier to digest. Changing the shape of the protein changes how that protein will interact with its environment.
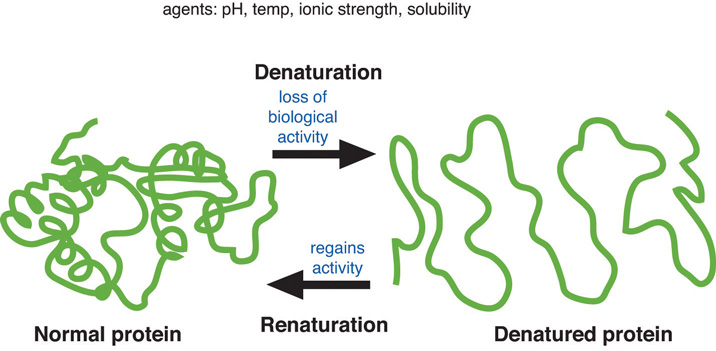
The opposite of denaturation is renaturation, when the protein or nucleic acid regains its secondary and or tertiary structure. This is not always possible.
An example of denaturation and renaturation is when Anfinsen denatured ribonuclease.
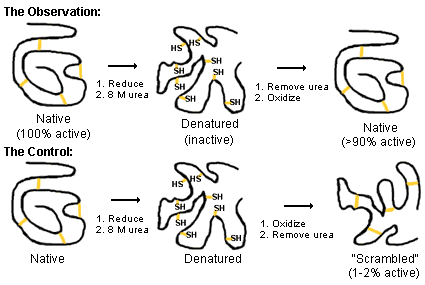
He used
Had Anfinsen removed the
Concept (but not wording) from Fundamentals of Biochemistry, Voet, Voet, and Pratt.


