Why does #cos(90 - x) = sin(x)# and #sin(90 - x) = cos(x)#?
2 Answers
Note that the image below is only for
If you wish you should be able to draw it with
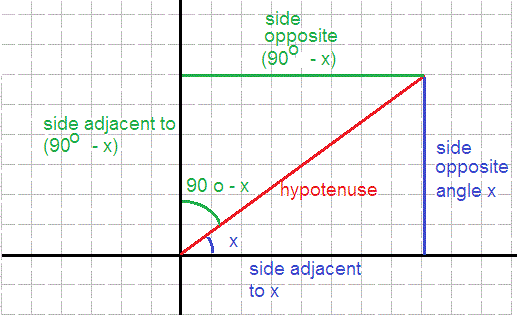
Definition of
#(# side opposite angle#x)//(# hypotenuse#)#
Definition of
#(# side adjacent to angle#(90^@-x))//(# hypotenuse#)#
but
Therefore
#sin(x) = cos(90^@ -x)#
Similarly
#cos(x) = sin(90^@ - x)#
These can also be proven using the sine and cosine angle subtraction formulas:
#cos(alpha-beta)=cos(alpha)cos(beta)+sin(alpha)sin(beta)#
#sin(alpha-beta)=sin(alpha)cos(beta)-cos(alpha)sin(beta)#
Applying the former equation to
#cos(90^@-x)=cos(90^@)cos(x)+sin(90^@)sin(x)#
#cos(90^@-x)=0*cos(x)+1*sin(x)#
#cos(90^@-x)=sin(x)#
Applying the latter to
#sin(90^@-x)=sin(90^@)cos(x)-cos(90^@)sin(x)#
#sin(90^@-x)=1*cos(x)-0*sin(x)#
#sin(90^@-x)=cos(x)#

