Question #74c1d
1 Answer
Explanation:
It's important to realize that the problem is asking for the average atomic mass of this sample of lithium, not of lithium in general.
There is a distinction between the two because this sample is depleted in the lighter isotope, which means that it contains less
So right from the start, you should expect the average atomic weight of lithium in this sample to be bigger than lithium's average atomic weight.
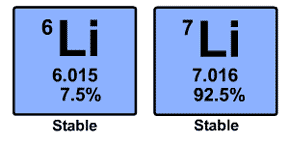
So, an element's average atomic weight is calculated by taking the weighted average of the atomic weights of its stable isotopes.
Each isotope will contribute to the average atomic weight proportionally to its abundance.
#color(blue)("avg. atomic weight" = sum_i "isotope"_i xx "abundance"_i)#
Now, to make calculations easier, you can use decimal abundances, which are simply percent abundances divided by
So, you know that this sample contains
#100% - 1.442% = "98.558% """^7"Li"#
The decimal abundances for the two isotopes will be
#"For """^6"Li: " (1.442%)/100 = 0.01442#
#"For """^7"Li: " (98.558%)/100 = 0.98558#
The average atomic weight of the sample will thus be
#"avg. atomic weight" = "6.0151122 u" xx 0.01442 + "7.016004 u" xx 0.98558#
#"avg. atomic weight " = color(green)(" 7.00157 u")#
So, is the average atomic weight bigger in this sample than what you would expect to see in a typical sample of lithium?
Indeed it is!
The average atomic weight for lithium varies between
As you can see, the sample depleted in the lighter isotope really does contain less