Question #58356
1 Answer
The colour is caused by the extended system of conjugated double bonds in the structures.
Explanation:
Structure
First, let's look at the structures of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and β-carotene.

Chlorophyll a and b contain a magnesium in a large ring system of conjugated double bonds that forms a large cloud of delocalized electrons.
The two chlorophylls differ in structure only in that one has an aldehyde group and the other has a methyl group.
β-Carotene also has an extended system of conjugated double bonds.
Light Absorption
These molecules can absorb photons of light.
If they absorb low-energy quanta (red light), the electrons are excited to a low energy level.
If they absorb high-energy quanta (blue light), the electrons are excited to a higher energy level.

Spectra
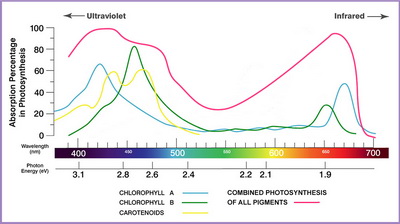
(from www.lushledlighting.com)
Chlorophyll a absorbs at 430 nm (blue-violet) and 662nm (red-yellow). It doesn't absorb green light, so it appears green.
Chlorophyll b has strong absorption at 453 nm (blue-violet) and 642 nm (red-yellow). It doesn't absorb from the mid-blue-green so it appears bluish green.
β-Carotene absorbs at 448 nm (blue) and 470 nm (violet). It doesn't absorb from the red-yellow region, so it appears yellow.

