Let's calculate those joint probabilities:
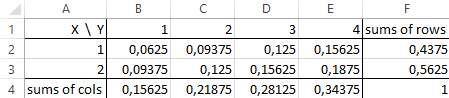
e.g. P(X=2 wedge Y=3)=0.15625.
It is now quite easy to obtain separate probability distributions of X and Y: we should sum rows or columns of area B2:E3, respectively, e.g.
P(X=2)=sum_(i=1)^4 P(X=2 wedge Y=i)=0.09375+ldots+0.1875=0.5625
Now we can use known formulas for the values we're looking for:
mu_x="E"X=1*0.4375+2*0.5625=1.5625
mu_y="E"Y=1*0.15625+2*0.21875+3*0.28125+4*0.34375=2.8125
"E"X^2=1^2*0.4375+2^2*0.5625=2.6875
"E"Y^2=1^2*0.15625+ldots+4^2*0.34375=9.0625
sigma_x^2="E"X^2-"E"^2X=2.6875-1.5625^2=0.24609375
sigma_y^2="E"Y^2-"E"^2Y=9.0625-2.8125^2=1.15234375
Now for the correlation coefficient rho we need the covariance sigma_(xy) so let's find the probability distribution of XY: (here p_(ij)=P(X=i wedge Y=j) )
P(XY=1)=p_(11)=0.0625
P(XY=2)=p_(12)+p_(21)=0.1875
P(XY=3)=p_(13)=0.125
P(XY=4)=p_(14)+p_(22)=0.28125
P(XY=5)=0
P(XY=6)=p_(23)=0.15625
P(XY=7)=0
P(XY=8)=p_(24)=0.1875
Now, for the covariance:
"E"(XY)=1*0.0625+ldots+8*0.1875=4.375
sigma_(xy)="E"(XY)-"E"X*"E"Y=-0.01953125
rho=(sigma_(xy))/sqrt(sigma_x^2*sigma_y^2)=-0.0366765706779718


