Acetylene is used in blow torches, and burns according to the following equation: 2 C2H2(g) + 5 O2(g) → 4 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) Use the following information to calculate the heat of reaction:?
Acetylene is used in blow torches, and burns according to the following
equation:
2 C2H2(g) + 5 O2(g) → 4 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g)
Use the following information to calculate the heat of reaction:
Hfo
(H2O(g))= -241.82 kJ/mol
Hfo
(CO2(g))= -393.5 kJ/mol
Hfo
(C2H2(g))=226.77 kJ/mol
Acetylene is used in blow torches, and burns according to the following
equation:
2 C2H2(g) + 5 O2(g) → 4 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g)
Use the following information to calculate the heat of reaction:
Hfo
(H2O(g))= -241.82 kJ/mol
Hfo
(CO2(g))= -393.5 kJ/mol
Hfo
(C2H2(g))=226.77 kJ/mol
1 Answer
Explanation:
Hess' Law states that the overall enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the route taken.
Thermodynamics is concerned with initial and final states and the law is a consequence of the conservation of energy.
You can solve this problem by constructing a Hess Cycle.
Write down the reaction you are interested in. Below this write down the elements from which the reactants and products are made.
Then complete the cycle as shown:
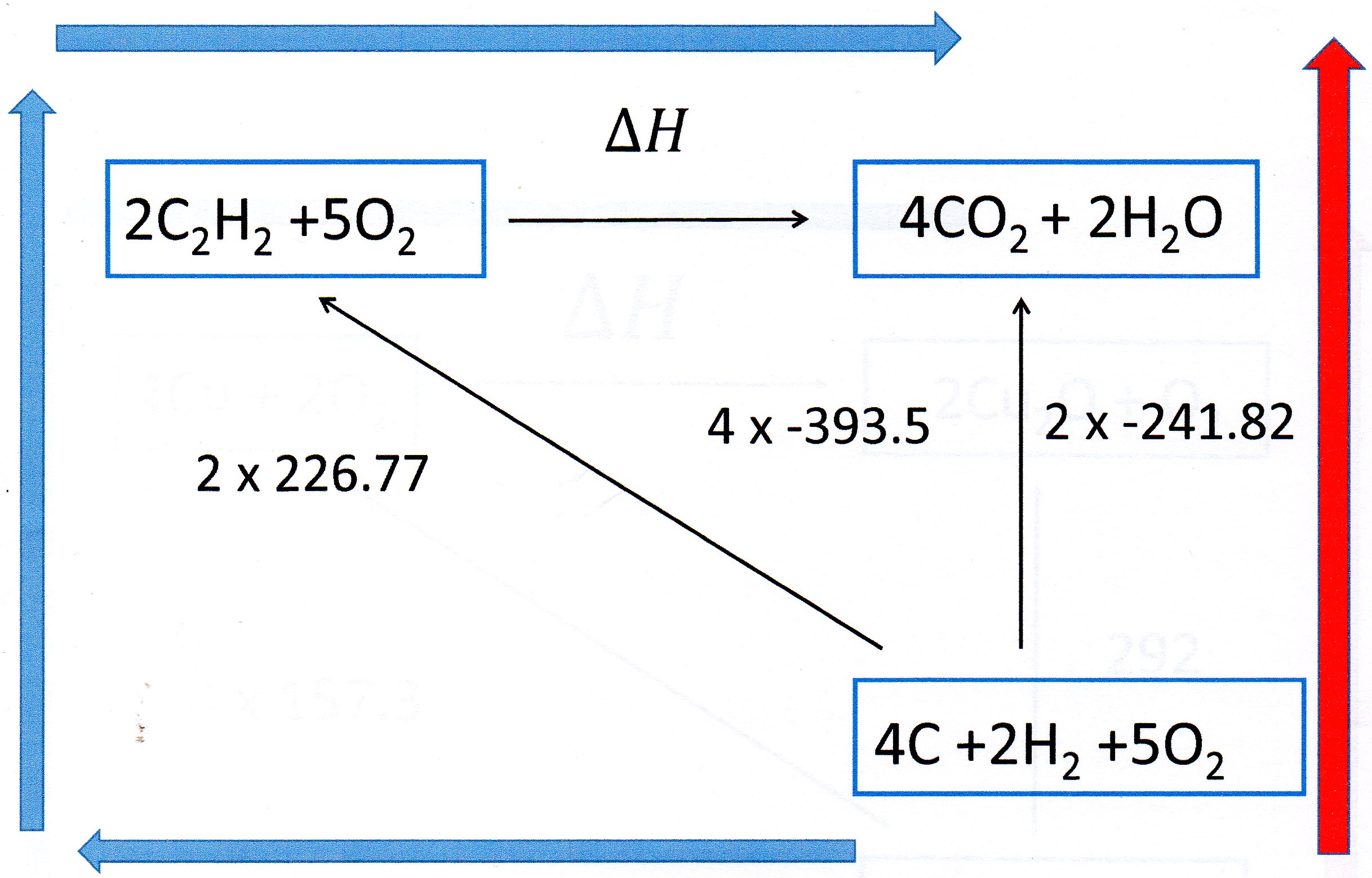
Notice I have multiplied the
In energy terms the
So we can write:

